1. Introduction
Skin is persistently subjected to environmental stressors, including ultraviolet (UV) radiation, which plays a significant role in the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Exposure to UV rays enhances ROS production within skin cells, potentially resulting in oxidative DNA damage, interference with normal cellular functions, and heightened inflammatory responses. These reactions accelerate skin aging by degrading collagen and elastin (Rinnerthaler et al., 2015). ROS also activate key signaling pathways such as MAPK and NF-κB, triggering inflammatory responses. Moreover, mitochondrial damage induced by ROS contributes to cell death and weakens skin structure (Min et al., 2024). In addition, UV exposure causes physical alterations in the skin, promoting melanin synthesis that leads to hyperpigmentation, and reducing the elasticity and flexibility of the dermis, which results in wrinkle formation and skin dryness. Modern society is increasingly exposed to external stressors such as industrialization and environmental pollution, which adversely affect the skin. These environmental stressors elevate oxidative stress and disturb the balance of the antioxidant defense system, accelerating the skin aging process (Santos et al., 2011). Consequently, consumers increasingly seek natural, clean, and plant-derived cosmetic ingredients with proven antioxidant and anti-aging benefits, driving demand for bioactive compounds such as polyphenols and flavonoids that support skin barrier integrity and resilience (Michalak, 2022). Marigold, a member of the Asteraceae family, is characterized by its yellow, orange, and golden petals. Common species include Tagetes erecta and Tagetes patula. Marigold extracts are recognized for their strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Notably, African marigold extract contains bioactive substances like lutein, flavonoids, and polyphenols, which play roles in reducing inflammation and enhancing collagen production, contributing to the prevention of skin aging (Park et al., 2017). Additionally, due to its high lutein content, marigold is widely used as a food colorant and as a supplement for eye health (Vallisuta et al., 2014).
Recently, various strategies have been explored to enhance the bioactivity of plant-based foods, which offer the advantages of low cost and high quality. Among these, fermentation of plant materials is considered a promising method not only for preservation but also for enhancing physiological activities (Taskila and Ojamo, 2013). Processes involving lactic acid fermentation are common in sectors such as dairy production, alcoholic drinks like wine and cider, the fermentation of vegetables, as well as in meat product processing (Taskila and Ojamo, 2013). Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) are microorganisms that primarily produce lactic acid through the breakdown of carbohydrates. Dominant in the human gut microbiota, LAB serve as probiotics that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria and suppress harmful ones. They are also reported to improve gastrointestinal functions, inhibit cholesterol absorption, enhance nutrient bioavailability, and regulate various physiological functions (Park et al., 2006). Although extensive research on antioxidant, anti-ulcer, and other health-related effects of marigold, limited work has focused on how fermentation with microorganisms influences its properties. This study aimed to produce fermented marigold extract through lactic acid bacterial fermentation and compare the antioxidant and anti-wrinkle activities of fermented and non-fermented extracts. We hypothesized that fermentation with lactic acid bacteria would enhance the antioxidant and anti-wrinkle activities of marigold extract. Lactobacillus plantarum (KCTC 3108), classified as a ‘Generally Recognized As Safe’ strain, was selected for fermentation in this study due to its excellent survivability and fermentation capability in plant-based substrates, as well as its reported ability to enhance antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities (Fei et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024). This study was conducted to investigate how lactic acid bacteria fermentation alters the antioxidant and anti-wrinkle properties of marigold extract. The objective was to determine whether fermentation enhances the biological activity of marigold, thereby supporting its potential application as a functional food or cosmetic ingredient.
2. Materials and methodology
Dried petals of marigold (Tagetes erecta), harvested in Egypt in 2023, were used as the raw material for the fermentation process. The L. plantarum strain KCTC 3108 was obtained from the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB; Daejeon, Korea) and cultured on de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) agar at 30°C for 24 h. Human dermal fibroblast cells (CCD-986sk) were procured from the Korean Cell Line Bank (KCLB; Seoul, Korea). These cells were maintained under standard conditions in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM), supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Gibco, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2. To analyze antioxidant capacity, the following reagents were employed: 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt (ABTS), gallic acid, and quercetin, all of which were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). For the assessment of anti-wrinkle efficacy, reagents including N-succinyl-Ala-Ala-Ala-p-nitroanilide and MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] were also purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Additionally, the Procollagen Type I C-peptide (PIP) EIA Kit used in the experiment was supplied by Takara Bio Inc. (Otsu, Japan).
Marigold was used as the substrate for fermentation. L. plantarum KCTC 3108 was cultured in MRS broth (Difco™ Lactobacilli MRS broth, BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) at 30°C with shaking at 120 rpm. The cultured bacteria were inoculated into the marigold and incubated for 7 days at 30°C to induce fermentation. After the fermentation period, microbial viability was confirmed, with a viable cell count reaching 5.3×108 CFU/g. To obtain the extracts, 70% ethanol was added to both fermented and non-fermented marigold samples in flasks, and extraction was carried out at 25°C for 24 h. The resulting solutions were designated as marigold ethanol extract (MEE) and fermented marigold ethanol extract (FMEE). Each extract was filtered through Whatman No. 2 filter paper (England), concentrated under reduced pressure using a rotary evaporator (LABOROTA 4000-efficient, Heidolph Instruments GmbH & Co. KG, Germany), and then freeze-dried for 72 h using a lyophilizer (EYELA, Tokyo Rikakikai Co., Tokyo, Japan). The dried extracts were used for subsequent experiments.
The total polyphenol content was measured using a modified method based on Folin and Denis’s study (1912). Briefly, 1 mL of the sample was mixed with 5 mL of distilled water, followed by the addition of 0.5 mL of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. After gentle mixing, the mixture was left to react for 8 min. Then, 10 mL of 7% sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) solution was added, and the total volume was adjusted to 25 mL with distilled water. The reaction mixture was incubated in the dark at room temperature for 2 h. Absorbance was recorded at 750 nm using a UV-Visible spectrophotometer (UV-1800, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The total polyphenol content was expressed as milligrams of gallic acid equivalents (mg GAE/g).
The total flavonoid content was determined following a modified protocol from Moreno et al. (2000). A 40 μL aliquot of the sample was combined with 80 μL of distilled water, and 6 μL of 5% sodium nitrite (NaNO2) was added. After incubating for 5 min, 12 μL of 10% aluminum chloride (AlCl3) solution was introduced, and the mixture was allowed to react for another 6 min. Subsequently, 40 μL of 1 N sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and 42 μL of distilled water were sequentially added. The solution was mixed thoroughly to prevent any precipitation. Absorbance was then measured at 510 nm using a spectrophotometer. Flavonoid content was calculated and expressed in milligrams of quercetin equivalents (mg QE/g).
The DPPH radical scavenging ability was measured using a modified method based on Dietz et al. (2005). Samples at various concentrations were mixed with 150 μL of 0.1 mM DPPH in methanol and incubated in the dark at room temperature for 30 min. Absorbance was recorded at 517 nm and the scavenging activity was calculated as follows:
The ABTS assay was performed using a modified protocol from Re et al. (1999). ABTS+ was produced by mixing equal volumes of 7 mM ABTS and 2.45 mM potassium persulfate, incubated in the dark for 12 h. The solution was diluted with 5 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) to an absorbance of 0.7 at 413 nm. Then, 40 μL of the sample was combined with 4 mL of diluted ABTS+ solution and reacted for 1 min. Absorbance was measured at 413 nm using L-ascorbic acid as a positive control. The scavenging percentage was calculated as:
The FRAP assay followed the procedure by Benzie and Strain (1996). The reagent was freshly prepared by mixing 300 mM acetate buffer (pH 3.6), 40 mM HCl, 10 mM TPTZ, and 20 mM FeCl3 ․ 6H2O in a 10:1:1 volume ratio. Each 0.5 mL sample was mixed with 3.5 mL FRAP reagent, and absorbance was measured at 593 nm initially and after 5 min incubation at 37°C. Reducing power was quantified against a FeSO4‧7H2O standard curve.
SOD-like activity was assessed based on Marklund et al. (1974). In a 96-well plate, 50 μL of sample at varying concentrations was mixed with 50 μL of 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.5) containing 10 mM EDTA and 50 μL of 7.2 mM pyrogallol. The mixture was incubated at 25°C for 45 min, and absorbance was recorded at 492 nm. The SOD-like activity was calculated using the formula:
Elastase inhibition was measured following Kang et al. (2011) with slight modifications. A 1.0 mM N-succinyl-Ala-Ala-Ala-p-nitroanilide substrate solution (1,300 μL) was prepared in 0.1 M Tris-Cl buffer (pH 8.0). Samples (7.5 μL) mixed with 92.5 μL buffer were added to the substrate and incubated at room temperature for 10 min. Afterward, 100 μL elastase (10 μg/mL) in 0.12 M Tris-Cl buffer was added to reach a final enzyme activity of 0.0025 U/mL. The reaction was incubated for 20 min at room temperature, and absorbance was recorded at 410 nm to evaluate inhibition.
Cytotoxic effects were assessed using the MTT assay. CCD-986sk human dermal fibroblasts were seeded at 1.3×105 cells/mL in 96-well plates and cultured for 24 h. The medium was replaced with 200 μL of different concentrations of MEE or FMEE, followed by 24 h incubation. After removing the medium, 200 μg/mL MTT solution was added, and cells were incubated in the dark at 37°C for 3 h. The MTT solution was discarded, cells were washed with PBS, and 200 μL DMSO was added to dissolve formazan crystals. Absorbance at 570 nm was measured using a microplate reader (Infinite M200 Pro, Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland).
Type I collagen synthesis was quantified using the Procollagen Type I C-peptide (PIP) EIA Kit on CCD-986sk cells. Wells were coated with 100 μL of antibody-POD conjugate, then 20 μL of MEE or FMEE-treated sample was added. Plates were incubated at 37°C for 3 h in the dark, followed by four washes with 400 μL washing buffer. Substrate solution was added and incubated for 15 min at room temperature. The reaction was stopped with 100 μL of 1 N H2SO4 and gently shaken for 1 min. Absorbance at 450 nm was measured, and collagen synthesis was calculated from a standard curve.
Data were processed using IBM SPSS Statistics (version 29, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). All experiments were performed in triplicate (n=3), and data are presented as mean±standard deviation (SD). One-way ANOVA was used to compare differences among groups, and Duncan’s multiple range test was used as a post-hoc analysis. Results were considered statistically significant at p<0.05.
3. Results and discussion
Table 1 presents the amounts of total polyphenols and flavonoids in the marigold extracts. The MEE contained 33.58 mg GAE/g of total polyphenols, while the FMEE exhibited a significantly higher content, reaching 77.37 mg GAE/g (p<0.001). The total flavonoid content increased from 27.21 mg QE/g in MEE to 40.74 mg QE/g in FMEE (p<0.01). These results indicate that fermentation effectively promoted the accumulation of bioactive compounds in marigold extracts. A similar trend was observed in a study by Park et al. (2018), where flaxseed ethanol extracts fermented with Lactobacillus brevis, Pediococcus pentosaceus, and L. casei showed increased levels of antioxidant compounds. Polyphenols and flavonoids are key bioactive compounds contributing to antioxidant activity. During fermentation, complex phenolic compounds can be hydrolyzed into low-molecular-weight forms by microbial enzymes, enhancing their bioactivity (Kim et al., 2018). According to Li et al. (2019), fermentation with L. plantarum enhances polyphenol content in fruit-based substrates by enzymatic hydrolysis, contributing to improved antioxidant activity. In this study, fermentation significantly elevated the levels of polyphenols and flavonoids in marigold extracts. This improvement in bioactive compound content is likely related to microbial enzymatic actions that facilitate the breakdown of cellular structures and liberate phenolic substances. According to prior research (Jeong et al., 2023; Kim et al., 2018), such enzymatic activity can increase the bioavailability of phytochemicals. The enhanced polyphenol and flavonoid contents in FMEE suggest its potential utility as a functional ingredient in health-oriented food products.
| Sample1) | Total polyphenol contents (mg GAE/g) | Total flavonoid contents (mg QE/g) |
|---|---|---|
| MEE | 33.58±0.022) | 27.21±0.89 |
| FMEE | 77.37±1.52***3) | 40.74±3.93** |
To assess antioxidant capacity, the DPPH radical scavenging ability of marigold extracts was measured, as presented in Fig. 1A. When treated at 100 μg/mL, MEE exhibited 24.59% scavenging activity, while FMEE showed a higher value of 29.55%. As the concentration increased, both extracts demonstrated enhanced radical scavenging performance, with FMEE consistently outperforming MEE at concentrations above 100 μg/mL (p<0.05). At the highest tested level (500 μg/mL), MEE and FMEE showed activities of 68.75% and 73.67%, respectively, reflecting a statistically significant difference (p<0.05). These results suggest that fermentation improves the antioxidant properties of marigold extracts. Similar findings were reported by Kim et al. (2012), who found that fermentation of garlic with L. plantarum elevated its antioxidant activity. Likewise, Li et al. (2024) demonstrated that lactic acid fermentation of Rosa rugosa enhanced antioxidant capacity through alterations in active compound profiles.
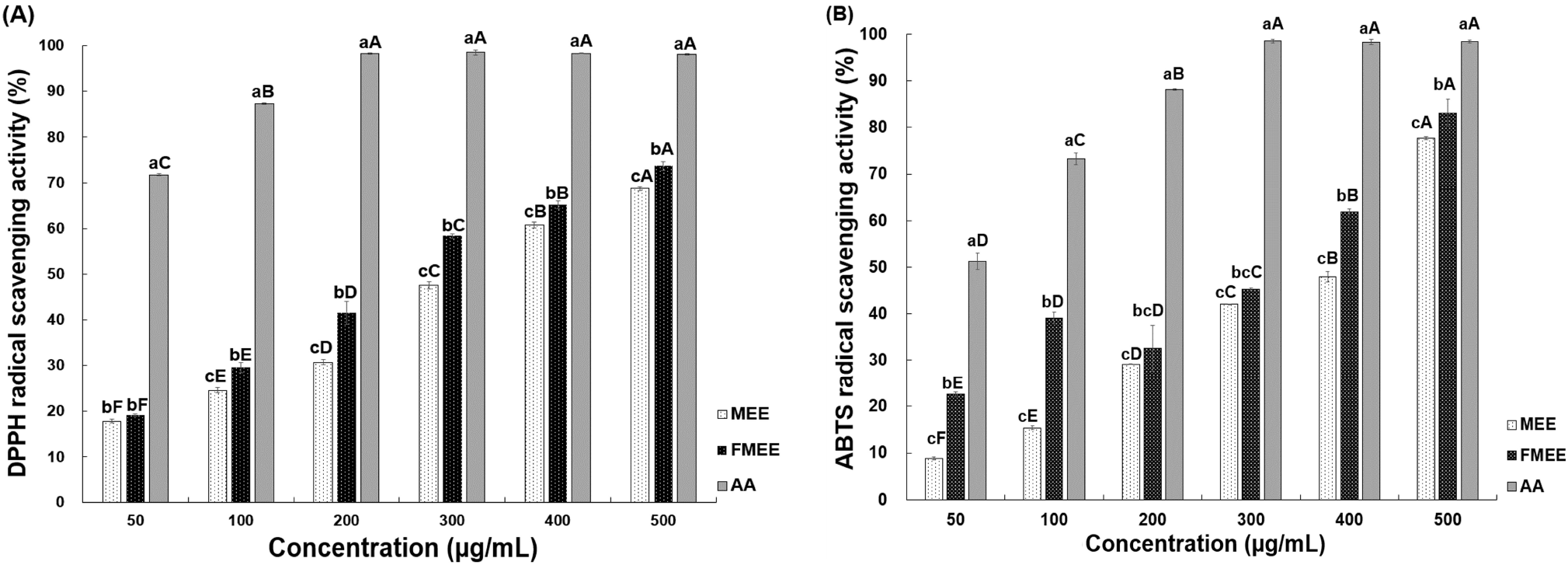
As shown in Fig. 1B, the ABTS radical scavenging capacity of marigold extracts increased with concentration. Both MEE and FMEE exhibited a concentration-dependent increase in ABTS scavenging activity (p<0.05). At 50 μg/mL, MEE showed the lowest activity at 8.86%, while FMEE displayed a significantly higher activity of 22.53%. At 500 μg/mL, MEE reached 77.72%, whereas FMEE recorded 83.10%, maintaining superior activity across all tested concentrations. Notably, at 50 μg/mL and 100 μg/mL, FMEE demonstrated more than double the ABTS scavenging activity compared to MEE, suggesting that fermentation enhanced the antioxidant capacity. This enhancement may be attributed to the increased levels of bioactive compounds such as polyphenols and flavonoids generated during fermentation. These findings align with those reported by Li et al. (2024), who demonstrated increased antioxidant effects in Rosa rugosa extracts fermented with L. plantarum. In particular, this trend is similar to the results obtained in the DPPH assay, suggesting consistent enhancement of antioxidant properties through fermentation.
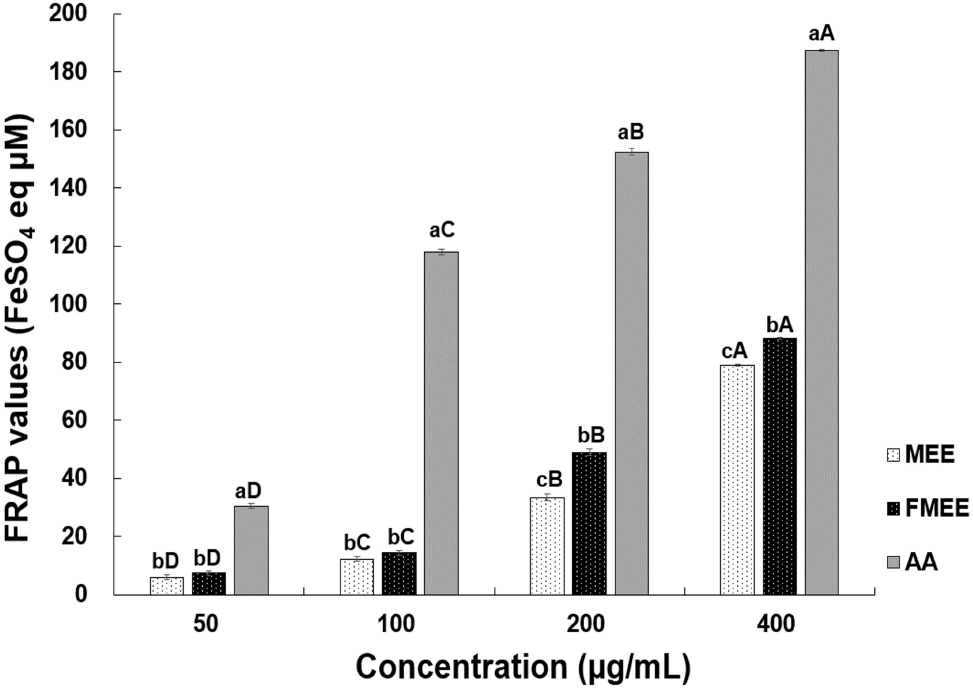
The FRAP analysis results for marigold extracts are shown in Fig. 2. All samples demonstrated a significant increase in FRAP values with rising concentrations (p<0.05). Above 200 μg/mL, a statistically significant difference was observed between MEE and FMEE. Especially, at 400 μg/mL, the FRAP value of FMEE (88.17 μM FeSO4 eq) was significantly higher than that of MEE (78.84 μM FeSO4 eq, p<0.05), consistent with the trend observed in radical scavenging assays. According to the study by Lee and Hong (2016), the FRAP reducing power increased when Morus (mulberry) was fermented with lactic acid bacteria, which was attributed to phenolic compounds and anthocyanins produced during fermentation. Similarly, Jeong and Oh (2022) reported increased reducing capacity in Ananas comosus fermented with L. plantarum. Thus, microbial metabolism likely contributed to the enhanced antioxidant capacity observed in FMEE.
SOD is an important enzyme responsible for detoxifying reactive oxygen species, and it is widely recognized for its beneficial effects in medicine and cosmetics, particularly due to its anti-aging properties (Michalak, 2022). The SOD-like activity results of the marigold extracts are presented in Table 2. As a positive control, ascorbic acid exhibited over 94% activity at all concentrations. MEE showed SOD-like activities of 34.02%, 39.78%, and 57.57% at 50, 100, and 300 μg/mL, respectively. In contrast, FMEE demonstrated significantly higher activities of 41.64%, 68.16%, and 72.97% (p<0.05). At 100 μg/mL, FMEE displayed approximately 1.7 times greater activity than MEE. These findings suggest that fermentation contributed to the enhancement of SOD-like activity in marigold extracts, likely due to the increased concentration of phenolic compounds and antioxidants produced during fermentation. FMEE also exhibited a concentration-dependent increase, with the highest activity observed at 300 μg/mL. These results support the potential of FMEE as a natural antioxidant ingredient.
The elastase inhibition rates are presented in Table 2. At 50 μg/mL and 100 μg/mL, there was no significant difference between the inhibition rates of MEE and FMEE. However, at 300 μg/mL, MEE demonstrated an inhibition rate of 25.14%, whereas FMEE showed a significantly higher inhibition rate of 31.03% compared to MEE (p<0.01). These results suggest that FMEE is more effective than MEE in inhibiting elastase activity, particularly at higher concentrations. This enhancement may be attributed to increased concentrations of flavonoids and polyphenols generated through fermentation, which interact with the elastase enzyme. Elastase is a matrix-degrading enzyme that breaks down elastin and collagen, accelerating wrinkle formation when overactive (Michalak, 2022). Excessive elastase activity has been associated with dermal matrix degradation and wrinkle formation (Vallisuta et al., 2014). Richelle et al. (2010) reported that natural pigments such as carotenoids and anthocyanins can inhibit elastase activity. Likewise, Tagetes erecta flower extracts were found to suppress elastase and tyrosinase activity (Vallisuta et al., 2014). Berries such as blackberry and blueberry, rich in anthocyanins, have also demonstrated anti-aging effects through elastase inhibition (Santos et al., 2011). Kang et al. (2011) observed that fermented extracts of Cudrania tricuspidata with B. licheniformis and B. subtilis showed significantly higher elastase inhibitory activity compared to non-fermented controls. Consistent with these findings, the fermented marigold extract in this study appears to enhance elastase inhibition, making it a promising candidate for wrinkle-improving cosmetic applications.
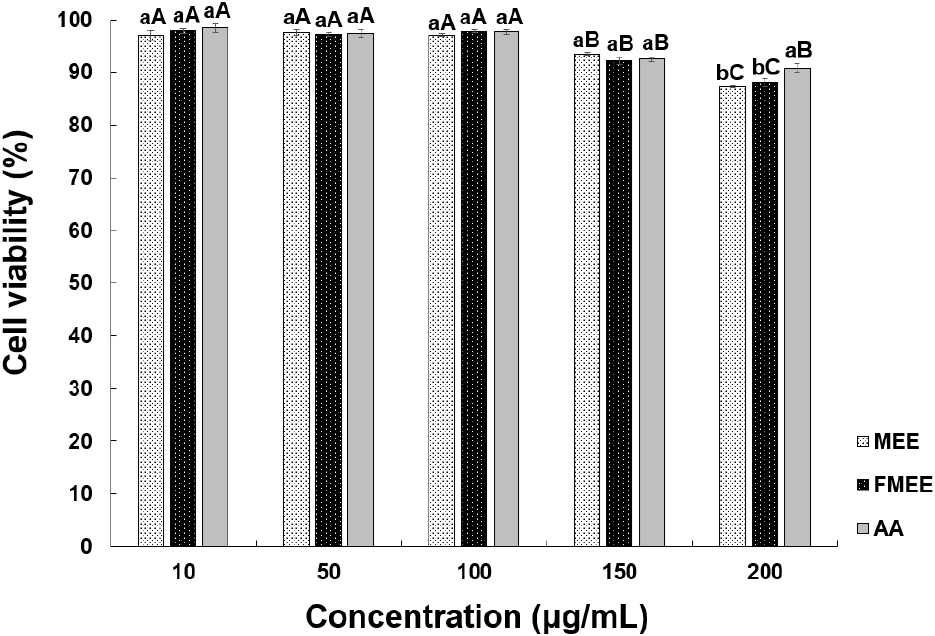
Cell-based efficacy testing was preceded by an evaluation of the cytotoxicity of marigold extracts using CCD-986sk human fibroblasts, as shown in Fig. 3. At 100 μg/mL, MEE and FMEE showed cell viabilities of 97.12% and 97.81%, respectively, with no significant difference. Both extracts showed decreased viability at concentrations above 150 μg/mL. According to Aldbass et al. (2021), exposure to plant-derived extracts at a similar concentration (~100 μg/mL) typically results in cell viabilities around 70-80%, consistent with our findings. In this study, cell viabilities of MEE and FMEE at the same concentration were 87.39% and 88.10%, respectively, indicating low cytotoxicity and suitability for subsequent wrinkle-improvement assays.
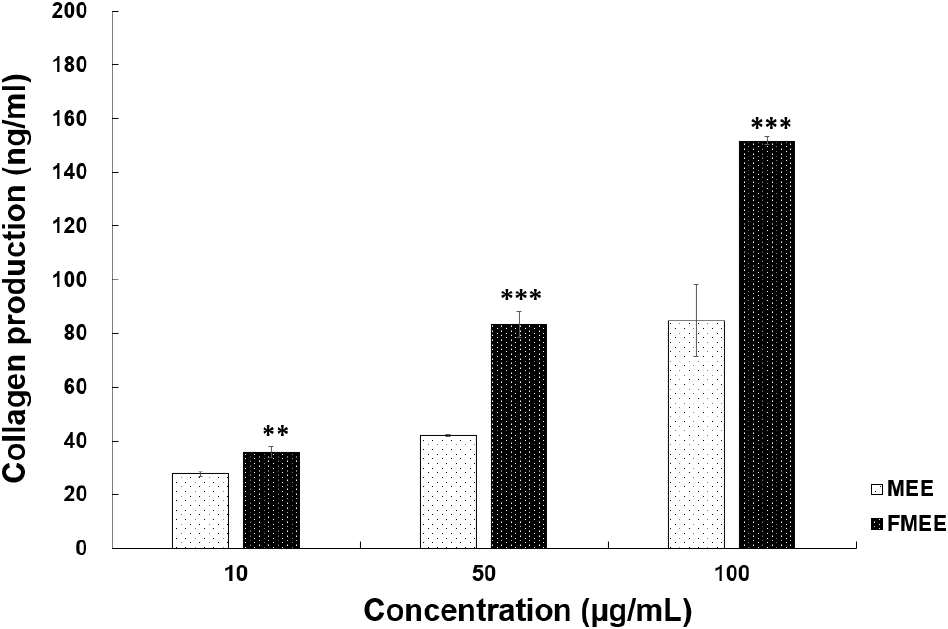
To assess the wrinkle-improving effect of fermented marigold extract, collagen production, which serves as an indicator of skin elasticity, was measured. As depicted in Fig. 4, at 10 μg/mL, MEE induced 27.61 ng/mL of collagen production, while FMEE induced a significantly higher level of 35.72 ng/mL (p<0.01). At 50 μg/mL, FMEE promoted collagen synthesis up to 83.28 ng/mL, nearly double that of MEE (41.83 ng/mL). At 100 μg/mL, FMEE further increased collagen synthesis to 151.78 ng/mL, compared to 84.78 ng/mL for MEE. These results suggest that fermentation significantly enhanced the bioactivity of marigold extract related to skin functionality. Fei et al. (2023) reported that Dendrobium officinale fermented with L. plantarum enhanced skin hydration, elasticity, and wrinkle reduction, highlighting increased functionality of bioactive compounds. Fermentation may promote bioconversion of functional compounds, thereby enhancing skin absorption and stimulating collagen synthesis. FMEE’s ability to stimulate collagen production highlights its potential use as a functional component in anti-aging skincare formulations.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that fermentation enhances the antioxidant capacity and skin-related functionality of marigold extracts. FMEE exhibited significantly higher antioxidant activities in DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP assays, along with enhanced SOD-like activity, elastase inhibition, and collagen synthesis, thereby confirming the effectiveness of fermentation in increasing functional components. These findings suggest that FMEE can serve as a promising natural material for functional cosmetics and health supplements. Despite these promising results, the present study is limited to in vitro conditions. Therefore, further in vivo and clinical investigations are necessary to confirm the efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of FMEE. Moreover, scale-up of the fermentation process and long-term stability assessments are essential for its industrial application in cosmetics and nutraceuticals.










