1. 서론
인간의 피부 노화는 특정 요인으로 인해 피부 세포의 활성이 저화 되는 상태로 나이가 들면서 피부 세포의 활동이 억제되는 내인성 노화와 햇빛, 자외선(ultraviolet, UV), 음주 등 외부 환경 요인으로 인해 발생하는 외인성 노화로 나뉜다(Farage 등, 2008; Zhang과 Duan, 2018). 이 중 자외선에 의한 노화 현상을 광노화라고 하며, 과도하거나 지속적인 자외선 노출은 피부에서 활성산소종(reactive oxygen species, ROS)의 생성을 촉진하게 된다(Chen 등, 2021; Krutmann 등, 2009). 자외선 노출에 따른 ROS의 증가는 피부의 탄력과 수분 공급 능력을 유지하는 콜라겐, 엘라스틴 등의 세포외 기질(extracellular matrix, ECM) 단백질을 분해하는 기질 금속단백분해효소(matrix metalloproteinase, MMP)의 발현을 강력하게 유도하여 궁극적으로 피부 주름의 형성을 촉진하고 주름을 유발하게 된다(Choi 등, 2020).
피부 진피층의 90%를 차지하는 콜라겐은 피부의 수분과 탄력을 유지하는 데 중요한 역할을 하며, 이 중 1형 콜라겐은 피부에 주로 존재한다(Nolte 등, 2007). 또한 히알루론산(hyaluronic acid, HA)은 수용성 다당류의 생체고분자로, 수분 보유 능력을 통해 조직의 수분 보유, 세포 성장 인자, 조직 치유 반응에 관여하는 것으로 보고되었다(Kim 등, 2007; Song 등, 2013). 현재 항산화, 피부미백, 주름개선 효과가 있는 것으로 알려진 기능성 물질은 식품산업, 화장품, 제약분야 등에서 상업적으로 널리 사용되고 있으나, 피부자극 및 체내 부작용을 유발하는 것으로 보고되어 안전하고 효과적인 천연 기능성 물질의 개발이 요구되고 있다(Kim 등, 2017).
안전한 천연소재 중 하나로 녹용(deer antler velvet, Cervi Parvum Cornu)보다 가격이 저렴한 녹각(deer antler, Cervi Cornu)은 항산화와 항염증 효과뿐만 아니라 운동 능력 향상에 유의미한 효과가 있는 것으로 알려졌으며(Kwon 등, 2017; Lee 등, 2015), 이를 이용한 건강 소재 개발에 대한 연구가 활발히 진행되고 있고(Ann, 2003; Park과 Lee, 2018), 최근 녹각 유래 콜라겐의 피부 건강 개선 효과가 추가적으로 확인된 바 있다(Goo 등, 2023). 전통 약재로 사용되어 온 구기자(Lycium chinense Miller)는 피부 미백 및 주름 개선 효과가 뛰어나며, 멜라닌 생성 억제와 엘라스타아제(elastase) 억제를 통해 피부 탄력 개선에 기여하는 것으로 보고되었다(Choi 등, 2014; Kim 등, 2011). 또한, 금은화(Lonicera japonica Flos)는 자외선으로 유도된 산화 스트레스로부터 피부를 보호하며, ROS 제거와 멜라닌 합성 억제 효과를 통해 항산화 및 미백에 유용한 천연 성분으로 평가받고 있다(Seo 등, 2014; Yu 등, 2017).
따라서 본 연구에서는 저분자 녹각 유래 콜라겐의 피부 건강 개선 기능성을 증진시키기 위한 방법 중의 하나로 약용식물인 구기자 및 금은화 소재와의 시너지 효과를 탐색하고자 하였다. 이에 따라 인간유래 각질형성세포(human keratinocyte celL, HaCaT)와 hairless mice (HR-1)에서 저분자 녹각 콜라겐 추출 복합물(NP-2007C)의 자외선(ultraviolet B, UVB) 조사 유무에 따른 광노화 억제 효과를 확인하고, 보습 및 주름 개선 효과를 평가하여 피부 건강 기능성 증진 소재로서의 가능성을 확인하였다.
2. 재료 및 방법
저분자 녹각 콜라겐 추출 복합물(NP-2007C)은 열수추출 후 효소가수분해 과정을 거친 저분자 녹각 콜라겐 분말과 구기자 열수추출 분말 및 금은화 열수추출 분말을 여러 비율로 혼합하여 제조된 형태로 ㈜한풍네이처팜에서 제공된 것을 실험에 사용하였다. 이때 저분자 녹각 콜라겐 분말은 러시아산 녹각을 구입한 다음, 파쇄하고 원재료의 약 5배에 해당하는 물을 투입한 후 90±10°C의 조건에서 3시간씩 6회 반복하여 추출하였다. 추출물은 5 마이크론 필터로 여과 및 60°C에서 감압농축과정을 거친 다음 50±5°C에서 4시간 동안 Endo-protease(Novozyme, Bagsvaerd, Denmark) 효소로 1차 가수분해하였다. 다음으로 50±5°C에서 4시간 동안 Exo-peptidase(Novozyme, Bagsvaerd, Denmark) 효소로 2차 가수분해 및 60°C에서 18시간 동안 건조과정을 거쳐 평균 1,409 Da 분자량(data not shown)을 가진 저분자 녹각 콜라겐을 분말 형태로 제조하였다. 또한 구기자 열수 추출 분말과 금은화 열수추출 분말은 각각 원재료의 약 10배에 해당하는 물을 투입한 후 95±5°C의 조건에서 3시간씩 2회 반복하여 추출하였고, 5 마이크론 필터로 여과, 60°C에서 감압농축 및 60°C에서 18시간 동안 건조과정을 거쳐 분말 형태로 제조하였다.
HaCaT 세포는 Cell Lines Service(CLS; Eppelheim, Germany)에서 구입하였다. 배지는 Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM; Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA)에 10% fetal bovine serum(FBS; Gibco)과 1% penicillin-streptomycin(Gibco)을 혼합한 것으로, 5% CO2, 37°C로 설정된 세포 배양기(Labtech, Gyeonggi-do, Korea)에서 배양하였다.
NP-2007C의 피부 보습 효과를 확인하기 위하여 NP-2007C를 hairless mice 체중 대비 50, 100, 150 mg/kg의 농도로 2주간 경구 투여하였다. 대조군(NC)은 생리식염수를 사용하였고, 양성대조군(PC)은 히알루론산을 체중 대비 50 mg/kg의 농도로 사용하였다. 또한, NP-2007C의 자외선으로부터 피부 보호 효과를 확인하기 위하여 hairless mice에 UVB을 조사한 후, NP-2007C를 체중 대비 50, 100, 150 mg/kg의 농도로 12주간 경구 투여하였다. UVB 조사는 Yun 등(2019)의 방법으로 실험 동물의 등 부분에 일주일에 세 번 UV Crosslinker CL-1000M (UVP, Cambridge, UK)을 사용하여 시행하였다. UVB 조사량은 75 mJ/cm2에서 시작하여 매주 최소 홍반량 1회씩 증가시키고 최종적으로 최소 홍반량 3회 강도로 총 10주 동안 조사하였다. 동물실험은 (재)전남바이오진흥원 천연자원연구센터 실험동물윤리위원회(No.JINR2204)의 승인을 받아 수행하였다.
HaCaT 세포 및 hairless mice 피부 샘플에서 프로콜라겐, MMP-1 및 히알루론산 함량을 측정하기 위하여 procollagen type I C-peptide ELISA assay kit(Takara Bio, Inc., Otsu, Japan), MMP-1 ELISA kit(R&D Systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA) 및 human hyaluronan ELISA kit(R&D Systems, Inc.)를 사용하여 제조업체의 프로토콜에 따라 수행하였다. 또한, 피부 샘플의 세라마이드 함량 측정은 human ceramide ELISA kit(MyBioSource, San Diego, CA, USA)를 사용하여 수행하였다. 그리고 피부 샘플에서 tumor necrosis factor alpha(TNF-α), interleukin-1β(IL-1β) 및 IL-6의 함량 측정은 각각 Mouse TNF-α ELISA kit(R&D Systems, Inc.), Mouse IL-6 ELISA kit(R&D Systems, Inc.) 및 Mouse IL-1β ELISA kit(R&D Systems, Inc.)를 사용하여 수행하였다.
UVB 조사를 통한 피부 손상 유발은 Ho 등(2022)의 방법으로 수행하였다. UVB 램프(Bio-Link BLX-312, Vilber Lourmat, Marne-la-Vallee, France)를 이용하여 HaCaT 세포에 UVB(30 mJ/cm2)를 조사한 후 NP-2007C를 25, 50, 100 μg/mL의 농도로 24시간 동안 처리하였다. 그 후, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase(CAT) 및 glutathione peroxidase(GPx) 활성을 측정하기 위해 각각 SOD assay kit, CAT assay kit 및 GPx activity assay kit(BioVision Inc., Milpitas, CA, USA)를 사용하여 분석하였다.
Hairless mice에 NP-2007C를 체중 대비 50, 100, 150 mg/kg의 농도로 2주간 경구투여한 후, comeometerⓇ CM 825(CK Electronics GmbH, Hamburg, Germany)를 사용하여 피부 수분함유량을 측정하였고, tewameter® TM 300(CK Electronics GmbH)를 사용하여 경피수분손실량(transepidermal water loss; TEWL)을 측정하였다. 또한, UVB를 조사한 hairless mice에 NP-2007C를 체중 대비 50, 100, 150 mg/kg의 농도로 12주간 경구투여한 후, visioline®(CK Electronics GmbH)을 사용하여 피부 주름을 평가하였다(Yun 등, 2019). 주름 지수 항목에는 총 면적, 총 길이, 주름 개수, 주름 깊이가 포함되었다.
Hairless mice의 피부 조직과 UVB를 조사한 HaCaT 세포에서 총 RNA 추출은 TRIzol(Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA)을 사용하였다. 추출된 RNA를 주형으로 사용하고 PrimeScriptTM RT master mix(Takara, Tokyo, Japan)를 사용하여 cDNA를 합성하였다. 그 후, 합성된 cDNA에 SYBR Green qPCR PreMIX (Enzynomics, Seoul, Korea)를 첨가하고 Rotor-Gene Q Real-Time PCR System(Qiagen, Hilden, Germany)을 사용하여 qRT-PCR을 수행하였다. 각 유전자의 발현 수준은 ΔCt(cycle threshold) 값을 사용하여 계산했으며 glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase(GAPDH)를 내부 대조군(internal control)으로 사용하였다.
3. 결과 및 고찰
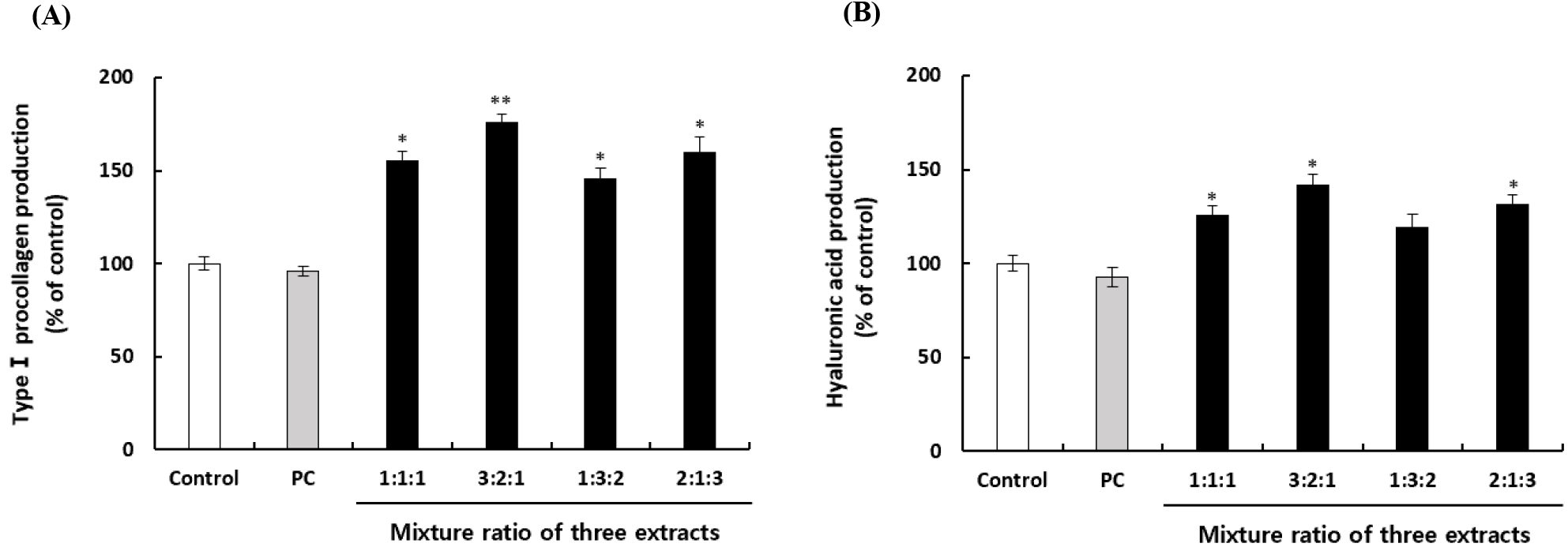
저분자 녹각 콜라겐 분말, 구기자 열수추출 분말 및 금은화 열수추출 분말의 피부건강 개선 기능성을 증진시키기 위한 최적배합조건을 확립하고자 HaCaT 세포에서 배합비율에 따른 프로콜라겐과 히알루론산의 생성량을 확인하였다. 노화에 의하여 감소되는 콜라겐과 히알루론산 함량을 유지하는 것은 피부 노화 억제의 가장 중요한 요인으로 간주되고 있다(Lee 등, 2013). 먼저 선행연구를 통해 처리농도를 100 μg/mL로 조정하였고, 녹각:구기자:금은화를 각각 1:1:1, 3:2:1, 1:3:2 및 2:1:3의 배합비율로 처리한 후 프로콜라겐 생성량을 확인한 결과 녹각:구기자:금은화 3:2:1의 처리구가 프로콜라겐 합성능이 우수한 것으로 나타났다(Fig. 1A). 또한, 히알루론산의 생성량을 확인한 결과 녹각:구기자:금은화 3:2:1의 처리구에서 히알루론산의 합성능이 우수한 것으로 나타났다(Fig. 1B). 이와 같은 결과를 바탕으로 저분자 녹각 콜라겐 분말, 구기자 열수추출 분말 및 금은화 열수추출 분말을 3:2:1의 비율로 혼합한 저분자 녹각 콜라겐 추출 복합물을 NP-2007C로 명명하였다.
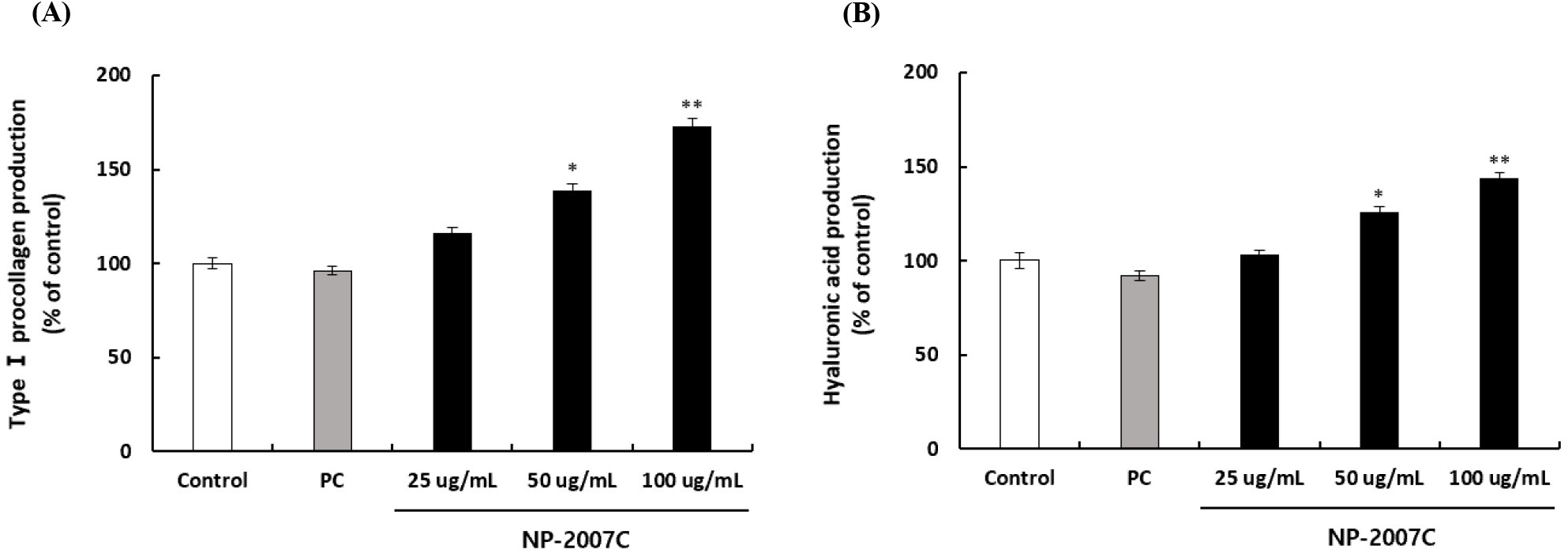
진피에 가장 풍부한 단백질은 콜라겐으로, 그 중 90% 이상이 프로콜라겐으로부터 생성된 콜라겐 타입 Ⅰ의 형태로 존재한다(Varani 등, 2001). 일반적으로 피부 세포를 포함한 다양한 조직과 세포에 존재하는 히알루론산은 염증, 세포 이동, 상처 치유에 중요한 역할을 하며, 세포막 단백질 효소인 hyaluronic acid synthase(HAS)에 의해 합성되는 것으로 알려져 있다(Jeon 등, 2014; Karvinen 등, 2003). 따라서 NP-2007C의 피부 보습 개선 효과를 확인하기 위해 HaCaT 세포를 이용하여 프로콜라겐과 히알루론산의 생성을 확인한 결과, NP-2007C 처리 수준이 증가함에 따라 프로콜라겐과 히알루론산의 합성이 증가하는 것으로 나타났다(Fig. 2). 또한, NP-2007C의 피부 보습 관련 유전자 조절 효과가 세포 수준에서 재현되는지 확인하기 위해 피부 보습 및 피부 장벽 기능과 관련된 주요 유전자의 발현을 qRT-PCR로 분석하였다. 그 결과, NP-2007C는 히알루론산 합성에 관여하는 HAS1, HAS2 유전자 발현, 세포 내로 수분을 운반하는 aquaporin 3(AQP3) 유전자의 발현, 피부 장벽을 보호하는 filaggrin 유전자의 발현을 증가시켜 피부 보습 개선 효과를 나타내는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 3).

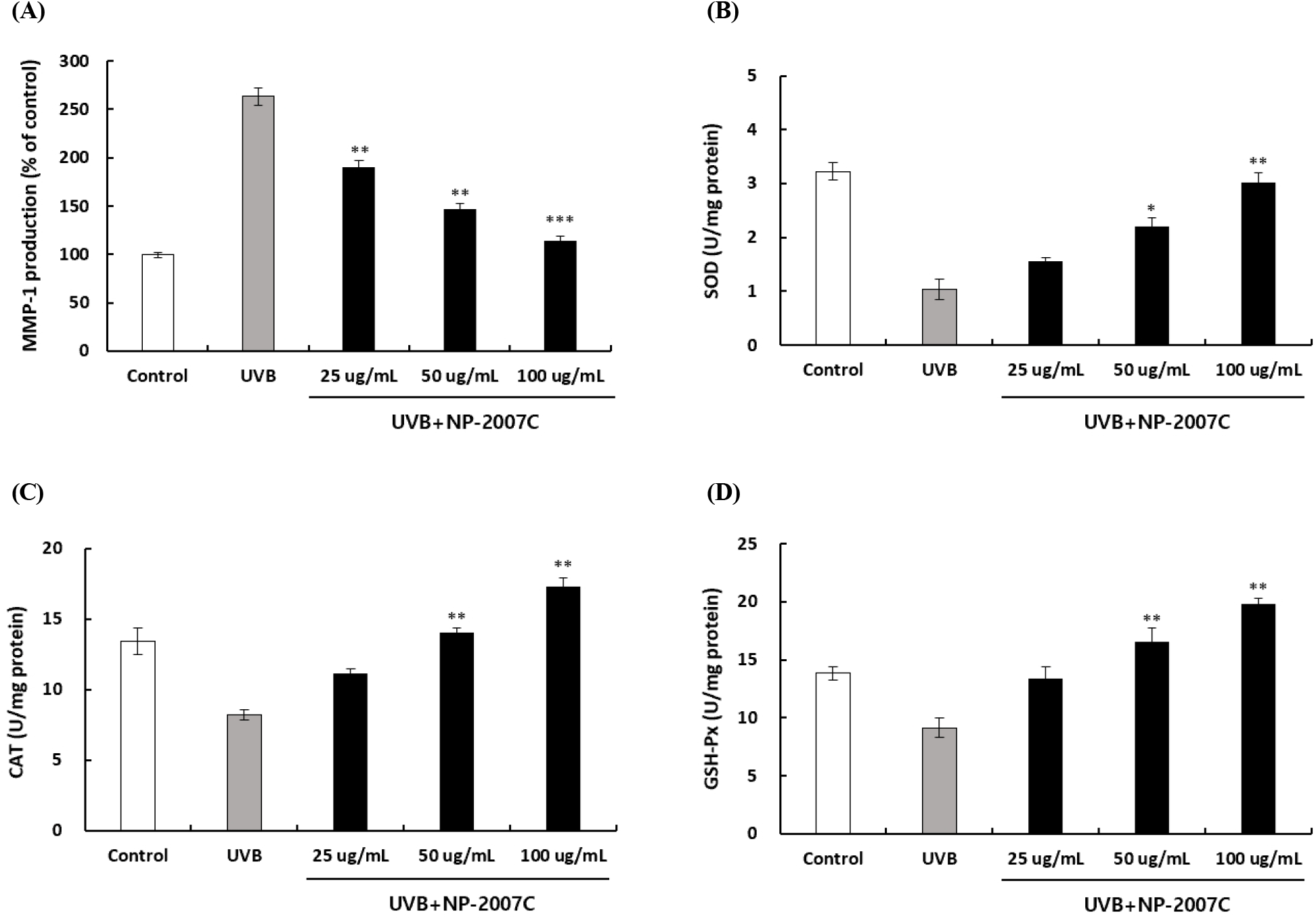
자외선에 의해 생성된 ROS의 축적은 mitogen-activated protein kinase(MAPK)의 인산화를 촉진하고, 인산화된 p38, jun N-terminal kinase(JNK) 등은 c-Fos와 c-Jun을 활성화시켜 activator protein-1(AP-1) 복합체를 형성하여 MMP와 같은 유전자의 발현을 조절한다(Choi 등, 2020; Lin 등, 2019; Son 등, 2011). 또한, 광노화 중에 발생하는 ROS의 생성과 이로 인한 MMP 발현의 증가 및 콜라겐 분해는 정상적인 ECM의 구조를 파괴하고 피부 주름 형성을 포함한 다양한 문제를 일으킨다(Chen 등, 2021; Kyrgidis 등, 2010; Pillai 등, 2005). 따라서 자외선에 의한 세포 내 ROS에 의해 생성된 matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) 등 콜라겐 분해 효소에 대한 NP-2007C의 저해 효과를 확인하기 위해 HaCaT 세포에 UVB를 조사하여 MMP-1의 생성을 측정하였다. 그 결과, NP-2007C 처리군은 UVB에 의해 유도된 MMP-1의 생성을 현저히 감소시켰으며, 이를 통해 NP-2007C의 자외선에 의한 주름 개선 효과를 확인하였다(Fig. 4A). 또한, 항산화 효소 활성을 확인하여 자외선에 의해 생성된 ROS에 대한 NP-2007C의 저해 활성을 확인하였다. 그 결과, NP-2007C 처리 수준이 증가함에 따라 UVB에 의해 유도된 항산화 효소 활성이 증가하는 것으로 나타났다(Fig. 4B-4D). 이러한 결과는 NP-2007C가 항산화 효소의 발현을 활발하게 유도하고 UVB에 의해 증가된 ROS를 감소시킴으로써 자외선으로 인한 피부 손상에 대해 보호 효과를 나타낸다는 것을 의미한다.
피부의 보습은 표피의 가장 외각에 존재하고 있는 각질층의 수분함량과 밀접한 관련이 있으며, 각질층의 수분함량이 저하되면 피부의 건조증상이 유발되어 피부장벽기능의 이상이 나타난다(Chang 등, 2007; Kwon 등, 2013). 따라서 NP-2007C가 피부의 수분유지와 손실량을 최소화하는 피부보습에 미치는 영향을 확인하기 위하여 NP-2007C를 hairless mice에 2주 동안 경구 투여하고, 피부 수분 함량과 TEWL을 측정하였다. 피부 수분 함량 측정 결과, NP-2007C 섭취군은 대조군에 비해 수분 함량이 유의하게 증가했으며(Fig. 5A), TWEL 측정 결과, NP-2007C 섭취군은 대조군에 비해 피부 수분 손실량이 유의하게 감소되는 것을 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 5B). 다음으로, 피부 조직에 발현되는 보습인자인 히알루론산과 세라마이드 함량을 측정한 결과, NP-2007C 섭취군에서 히알루론산과 세라마이드 함량이 유의하게 증가하여 NP-2007C 섭취를 통해서 피부보습이 개선되는 효과를 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 5C와 5D). 특히 열수추출 후 효소처리과정을 거친 저분자 녹각 콜라겐 팹타이드는 생체 내 분포하는 다이펩타이드나 트리펩타이드 함유량이 높아 체내 흡수 효율을 높이고 피부로의 빠른 분포를 유도하기에 우수한 피부보습 효과를 기대할 수 있다(Jung 등, 2021).

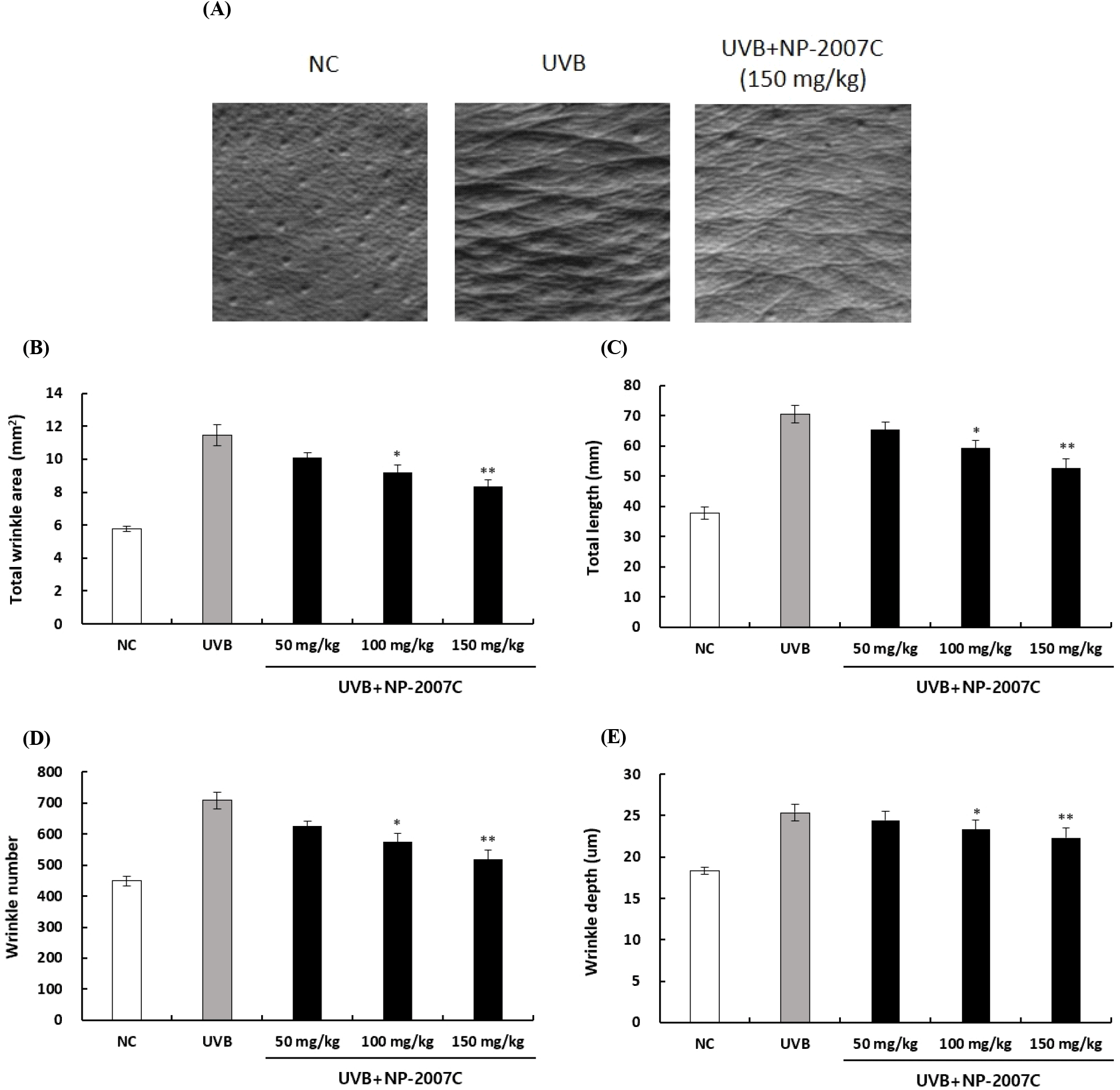
광노화는 피부 노화 손상의 주요 원인으로, 만성적인 자외선 노출로 인해 발생하며, 건조함과 주름 형성으로 이어진다(Chen, 2021; Poon, 2015). NP-2007C가 UVB 조사로 인한 피부 주름 변화에 미치는 효과를 확인하기 위해, hairless mice에 12주 동안 UVB를 조사하는 동시에 NP-2007C를 경구투여 하였다. 그 결과, NP-2007C 섭취군의 총 면적, 총 길이, 주름 개수, 주름 깊이가 현저히 감소하였다(Fig. 6). 이러한 결과는 자외선 조사로 인한 주름 형성이 NP-2007C에 의해 억제되었음을 나타낸다. 특히 구기자 성분 중 phytoestrogen은 estrogen과 유사하게 작용하여 estrogen 감소를 방지하고 이를 통해 지질 조성 및 collagen 합성을 유지하여 피부 탄력과 주름을 방지한다고 알려져 있다(Choi 등, 2014). 금은화의 주요성분 중에 하나인 chlorogenic acid 역시 UVB로 유도된 산화적 손상으로부터 ROS를 억제하고 산화스트레스로 인해 발생하는 자유 라디칼로부터 세포를 보호하여 피부 노화를 지연시키는 것으로 여겨진다(Cha 등, 2014).
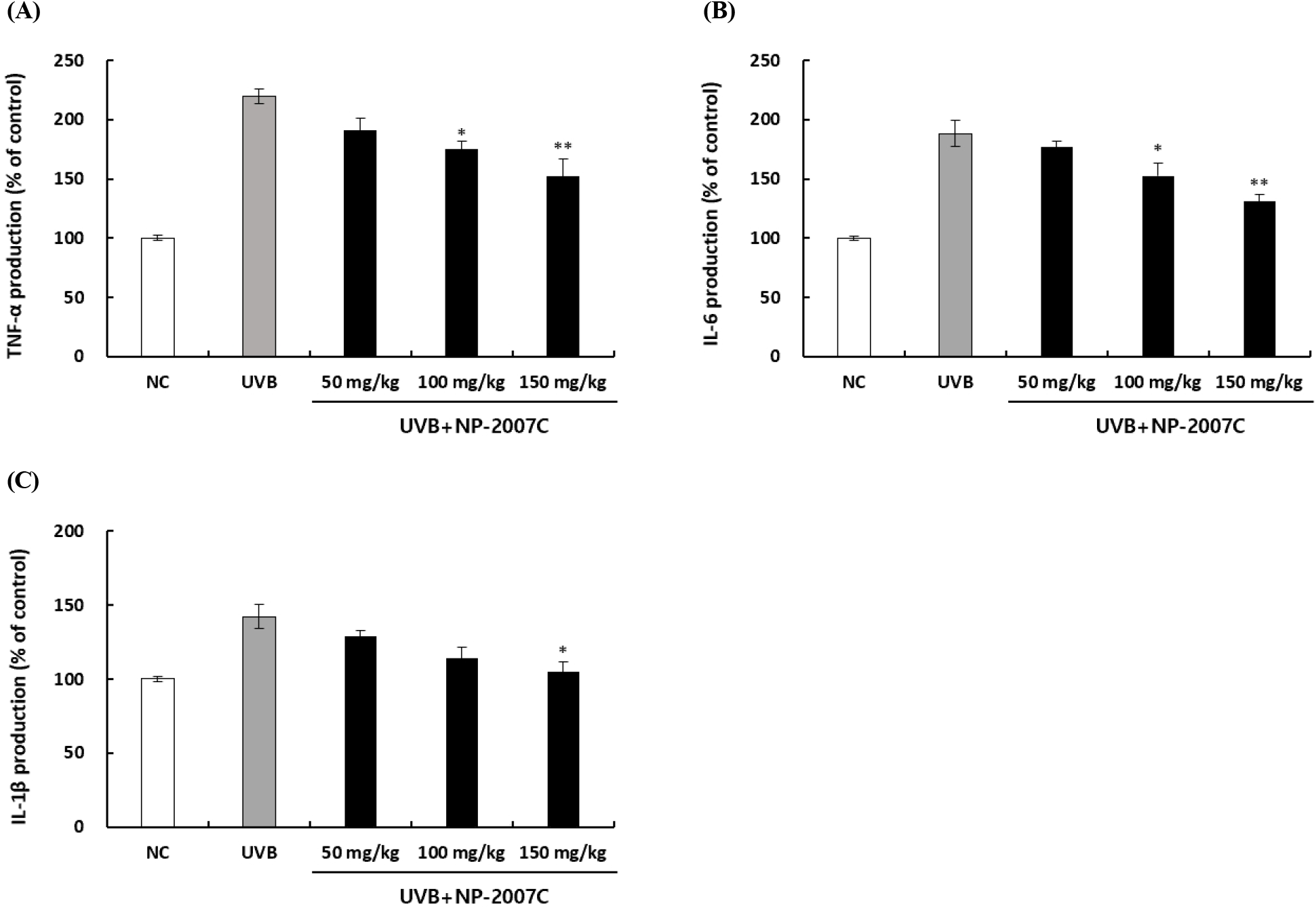
한편, 자외선 조사는 MAPK 신호 전달 경로를 조절하여 피부의 MMPs를 증가시켜 ECM 단백질을 분해한다(Han 등, 2022). 또한 MMP의 전사인자인 nuclear factor-κB(NF-κB)는 TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 등의 염증성 사이토카인을 증가시켜 피부 손상에 기여한다고 보고되었다(Yamamoto와 Gaynor, 2004). 따라서 hairless mice에 12주 동안 UVB를 조사하는 동시에 NP-2007C를 경구투여한 후 염증성 사이토카인 분비에 미치는 효과를 확인하였다. 그 결과 UVB를 조사군에서 정상 대조군에 비해 TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 분비가 유의하게 증가하여 사이토카인 분비가 유도되었으나, NP-2007C 섭취군은 염증성 사이토카인의 생성을 유의하게 억제하여 염증 반응 조절을 통해 피부 주름 형성을 억제하는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 7).
4. 요약
HaCaT 세포와 hairless mice에서 NP-2007C의 피부 건강 개선효과를 확인하였을 때, NP-2007C는 세포 및 생물학적 수준에서 항산화 효소 활성을 증가시켜 자외선 조사로 인한 산화 스트레스를 억제하였다. 또한 HAS1, HAS2, filaggrin, AQP3의 유전자 발현을 조절하여 프로콜라겐 타입 I과 히알루론산의 함량을 증가시켰고, 궁극적으로 MMP에 의한 콜라겐 분해를 억제하고 염증성 사이토카인의 활성을 감소시켜 피부 주름 형성, 수분 손실, 피부 탄력 감소와 같은 모든 광노화 증상을 개선하였다. 따라서 이러한 결과를 종합적으로 판단할 때 NP-2007C는 피부 보습 및 자외선으로 인한 피부 손상 개선을 위한 피부 건강 기능성 증진 소재로 효과적으로 활용될 수 있음을 확인하였다.










