서 론
댕댕이(Lonicera coerulea L.)는 인동과(Caprifoliaceae) Lonicera속에 속하는 쌍떡잎식물의 열매이며, 댕댕이 나무 는 시베리아, 사할린, 중국북부, 티베트, 북한 등지에 약 180여 종 생육하고 있는 냉대성 식물이다(1). 국가생물종지 식정보시스템에 따르면, 주요 품종에는 개들쭉(Lonicera coerulea var. emphyllocalyx), 넓은잎댕댕이(Lonicera coerulea var. longibracteata), 둥근잎댕댕이(Lonicera coerulea var. venulosa) 등이 있다. 댕댕이의 주성분은 saccharides(7.2%), lipids(1.52%), organic acids(12.2%)이며, 기능성 성분으로 는 polyphenols, ascorbic acid, vitamin B, magnesium, phosphorus, calcium, potassium 등이 포함되어 있다(2). 댕댕 이는 헛개나무 추출물과 함께 섭취하면 급성 알코올 중독을 해소하는 데 도움이 되며(3), 또한 허혈성 뇌혈관질환의 예방 또는 개선에도 도움을 줄 수 있다(4). 댕댕이의 주요 약리성분에는 phenolic acids, anthocyanins, flavonoids 등 phenolic compounds가 다량 함유되어 있으며 phenolic acids 중에는 chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid 등이 있고, anthocyanins에는 cyanidin-3-glucoside, cyanidin-3-rutinoside, cyanidin-3,5-diglucoside, peonidin-3,5-diglucoside, peonidin-3- glucoside 등이 있으며, flavonoids에는 rutin, quercetin, epicatechin 등을 포함한다(2). 이 화합물들은 과일이나 채소 에 색을 부여하며 인간의 건강에 유익한 영향을 주는데, 구체적인 이들의 생리활성으로는 항산화, 항암, 항균, 항알 러지, 항변이원성 및 항염증 효과 등이 있으며, 심혈관 질환 및 심장병의 위험도를 감소시킨다는 임상 결과도 보고된 바 있다(5). 천연자원에서 보다 많은 기능성 성분을 추출하기 위해 주로 이용되고 있는 추출방법은 압착법(expression), 환류추출법(reflux extraction), 압력추출법(pressure heating water extraction) 및 초임계유체추출법(supercritical fluid extraction)이 많이 사용되고 있다(6). 압착법은 장치와 조작 이 간단하나 수율이 낮으며, 환류추출법은 많은 용매가 필 요하며 추출 및 농축과정에서도 많은 시간을 필요로 한다. 압력추출법은 100℃이상의 고온에서 추출하므로 열에 민 감한 성분은 분해되어 소실되기 쉬우며, 초임계유체추출법 은 추출속도가 빠르며 용매의 소비가 적지만 비용이 많이 든다. 이러한 추출방법의 문제점을 보완하기 위하여 마이 크로웨이브추출법(microwave-assisted extraction, MAE)이 사용되고 있다(7). MAE 추출은 적은 용매와 에너지를 사용 하여 단시간에 원하는 물질을 추출할 수 있어 기존의 환류 추출법을 비롯한 soxhlet추출법, 압력추출법, 초임계유체추 출법 등에 비해 추출 효율 및 에너지효율이 우수하며, 순도 높은 기능성성분을 추출할 수 있어 환경친화적인 특징과 경제성을 지니고 있는 것으로 보고되고 있다. 이러한 microwave 처리 및 추출법의 특성으로 인하여 단백질의 변성이나 비타민의 파괴를 감소시킬 수 있고, 향기성분의 손실이나, 색소의 파괴를 막을 수 있는 장점으로 주로 식품 의 조리, 가공, 건조, 살균, 보존 및 효소의 불활성화를 위해 다양하게 사용되고 있다(8). 이에 본 연구는 댕댕이의 기능 성성분을 추출하기 위한 최적의 추출조건을 알아보기 위하 여 기존의 추출방법보다 추출효율 및 에너지효율이 좋은 것으로 알려져 있는 MAE 추출장치로 에너지강도와 추출 시간을 상이하게 하여 에탄올을 용매로 추출하고, 실험구 간의 유의성을 확인하기 위해 SAS software(SAS, Version 9.2, SAS Institute lnc., Cary, NC, USA)를 사용하여 수학적 통계방법에 의해 모델링을 한 뒤 반응표면분석법(response surface methodology, RSM)을 이용해 추출조건을 최적화하 였다.
재료 및 방법
본 연구의 실험재료인 댕댕이는 경북 문경에서 2014년 5월 말에 갓 수확한 것을 구입하였다. 댕댕이 시료는 동결건 조를 한 뒤 분쇄하여 40 mesh 통과분을 지퍼백에 넣어 극저 온냉동고(SW-UF-500P, Samwon Co., Busan, Korea)에 보관 하였다.
마이크로웨이브 추출은 2,450 MHz주파수의 실험용 상 압형 추출장치(Soxwave 100, Prolab, Fontenay, France)를 이용하여 programmable power(60-300 W)와 시간제어가 가 능하고 환류냉각관이 장착된 추출장치를 사용하였다. 추출 방법은 Fig 1과 같이 extraction vessel에 1 g의 시료와 용매 50 mL를 가한 후 추출공정에 변수를 조절하여 추출하고 여과지(Whatman No. 1, Whatman Co., Maidstone, UK)를 사용하여 흡입여과 한 후 100 mL의 부피로 하여 분석용 시료로 사용하였다.
본 실험은 반응표면분석법(RSM)을 이용하여 최적 추출 조건의 예측과 추출조건에 따른 추출물의 기능성 성분 함량 을 모니터링 하였다. 본 실험에서 중심합성계획법(central composite design, CCD)를 통해서 추출공정에 중요한 독립 변수(Xi)로 고려되는 인자 즉, 용액 농도(X1), 추출시간(X2) 및 microwave power(X3)에 대한 실험범위를 설정하여 각각 을 5단계로 부호화 하였으며(Table 1) 중심합성계획에 따라 Table 2와 같이 20구로 설정하여 추출실험을 하였다. 또한 이들 독립변수에 영향을 받는 종속변수(Yn) 즉, 총 플라보 노이드 함량(Y1), 총 안토시아닌 함량(Y2), 총 폴리페놀 함 량(Y3), DPPH 라디칼 소거능(Y4)을 측정하여 그 값을 회귀 분석에 사용하였다. 또한 추출조건이 댕댕이의 기능성성분 의 추출특성에 미치는 영향을 예측된 모델식을 바탕으로 mathematica program(Mathematica, Wolfram, Champaign, IL, USA)을 이용하여 4차원 반응표면분석으로 해석하였다.
| Xn | Response variables | Levels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -2 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||
| X1 | Ethanol concentration (%) | 0 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 |
| X2 | Irradiation time (min) | 1 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 13 |
| X3 | Microwave power (W) | 180 | 210 | 240 | 270 | 300 |
댕댕이 내 총 플라보노이드 함량(TFC)의 측정은 aluminum colorimetric assay(9)를 사용하였다. 댕댕이 추출물 70 μL에 증류수 430 μL를 가한 뒤 5% NaNO2 50 μL를 첨가하였다. 그리고 10% Al(NO3)3․9H2O를 가한 뒤 상온에서 6분간 반응시킨 후 1 N NaOH 500 μL를 첨가하였다. 반응액의 흡광도는 510 nm에서 UV-spectrophotometer(Shimadzu Co., UV-2550, Tokyo, Japan)를 이용하여 측정하였다. 표준물질 로 rutin(Sigma-Aldrich)을 이용하여 검량곡선의 작성에 사 용하였다.
총 안토시아닌 함량(TAC) 측정은 Truong 등(10)의 실험 방법을 참고하여 측정하였다. 댕댕이 추출물을 각각 500 μL 0.025 M potassium chloride(pH 1.0)와 0.4 M sodium acetate(pH 4.5)를 가하여 10배 희석한 1 mL 반응액을 만들 고 상온에서 15분간 반응시킨 후 UV-spectrophotometer (Shimadzu Co.)를 이용해 흡광도 값 530 nm, 700 nm에서 각각 측정하였다. 측정한 값을 다음 산도차등분석식을 이 용하여 산출하였다.
댕댕이 추출액의 총 폴리페놀 함량(TPC)은 Folin-Denis 법(11)을 변형시켜 측정하였다. 먼저 추출액 100 μL에 50 μL Folin-Ciocalteu reagent(Sigma-Aldrich)용액을 가한 뒤 300 μL의 2% Na2CO3를 넣고 실온에 15분간 반응시켰 다. 반응이 종료되면 1 mL의 증류수를 넣은 후, UVspectrophotometer( Shimadzu Co., UV-2550, Tokyo, Japan) 를 이용해 흡광도 값을 725 nm에서 측정하였다. 검량곡선 은 gallic acid(Sigma-Aldrich)를 표준물질로 작성하였으며, 측정결과는 mg of gallic acid equivalent per g(mg GAE/g)로 나타내었다.Table 3Table 4
댕댕이 추출액의 DPPH 라디칼 소거능 측정은 Blois의 방법(12)을 변형하여 사용하였다. DPPH radical scavenging activity 측정을 위해 DPPH 시약은 빛을 차단한 상태에서 0.0039 g에 에탄올 100 mL를 가한 후 magnetic stirrer (PC-420D, Corning Co., NY, USA)을 이용하여 2시간 동안 용액을 안정화시켜 사용하였다. 그리고 제조한 DPPH용액 900 μL에 댕댕이 추출물 100 μL을 가한 뒤 30분 동안 암실에 서 반응시켰다. 반응이 완료된 시약은 UV-spectrophotometer 를 사용해 517 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하였다. 측정한 값은 다음과 같은 식을 이용해 DPPH 라디칼 소거능을 산출하 였다.
결과 및 고찰
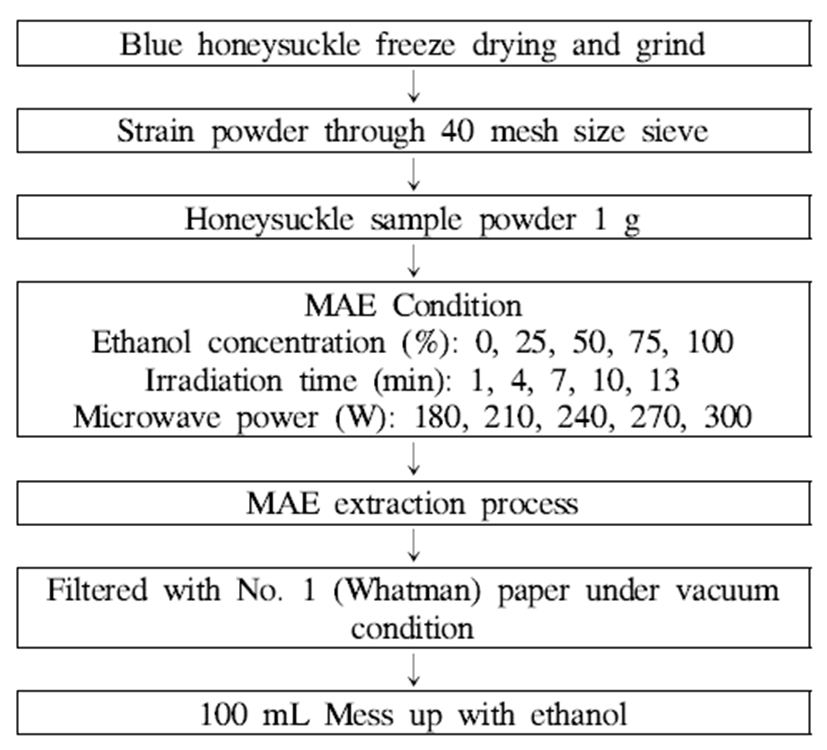
각 조건에 따른 댕댕이 추출물의 총 플라보노이드 함량 은 Table 2와 같으며 적합 모델식은 아래에 나타내었다.
댕댕이 추출물의 적합 모델의 R2은 0.95이었으며 0.1%이 내에서 유의성을 나타내었다. 이러한 회귀식을 바탕으로 총 플라보노이드 함량의 최대값은 에탄올의 농도 52.9%, 추출시간 7.5 분 및 microwave power는 248 W일 때 65.74 mg RE/g로 예측되었다(Table 5). 총 플라보노이드 함량에 영향을 미치는 조건은 에탄올의 농도와 추출 시간이었으며 microwave power는 플라보노이드 함량에 큰 영향을 나타내 지 않았다(Fig. 2). Kim 등(13)의 야관문의 경우에도 에탄올 농도가 영향을 준다고 보고를 하였으며, 용매의 농도가 결 정적인 요인이었다는 연구결과와 유사한 경향을 나타내었 다. 반면에 Lee 등(14)의 결과에서는 마이크로웨이브 파워 가 쥐깨풀 유용성분을 추출하는데 영향을 미친다고 보고하 여 본 실험과는 반대의 결과를 나타내었다.
| MAE conditions | Predicted optimal condition |
|---|---|
| Ethanol concentration (%) | 53-64 |
| Irradiation time (min) | 7.4-7.9 |
| Microwave power (W) | 242-250 |
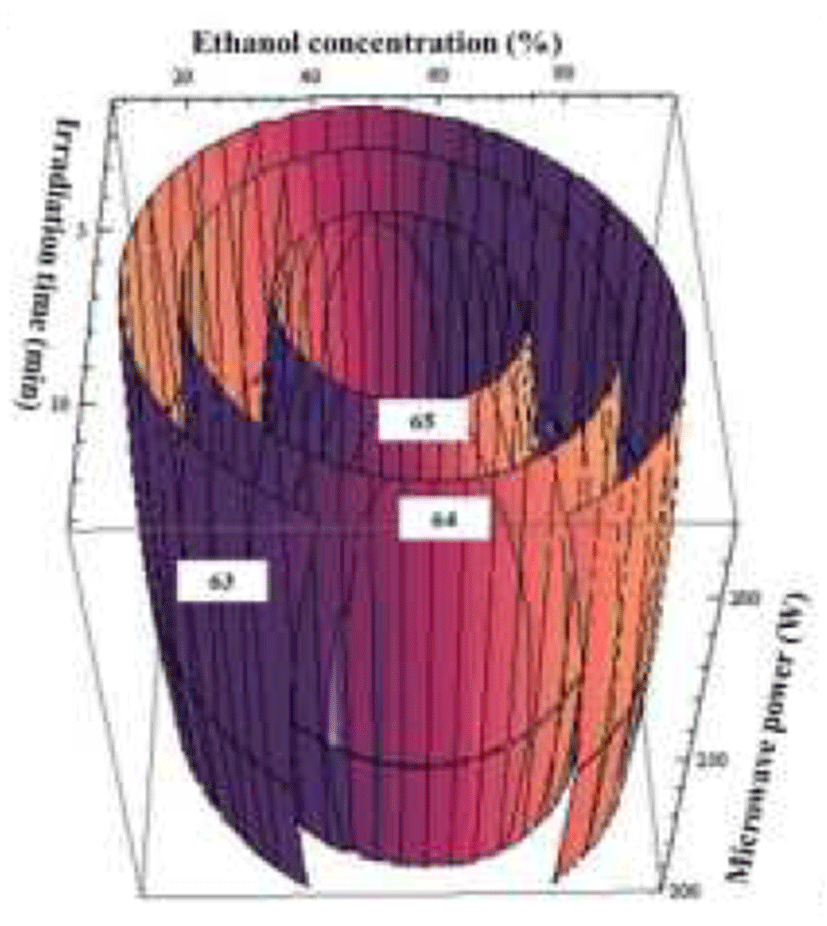
안토시아닌은 강력한 항산화 활성, 항염증, 항암 등 다양 한 생리활성에 대한 기적이 보고되고 있다(15). 각 조건에서 추출한 댕댕이 추출물의 총 안토시아닌 함량은 Table 2와 같다. 이러한 결과를 통해 추출조건에 따른 총 안토시아닌 함량에 대한 적합 모델식은 아래와 같다.
댕댕이 추출물의 총 안토시아닌 함량에 따른 추출물의 회귀식의 R2은 0.97이고 유의성은 0.1%이내의 수준에서 유의성을 나타내었다. 추출물의 안토시아닌 함량에 대한 최대값은 에탄올의 농도 54.8%, 추출시간 7.4분 및 microwave power 248 W일 때 0.45 mg CGE/g으로 예측되었 다(Table 5). Hong(16)의 논문에서 acai에 함유된 phenolic 성분은 에탄올 농도가 증가할수록 증가한다고 보고 하였으 며 본 결과와 유사한 경향을 나타내었다(Fig. 3).
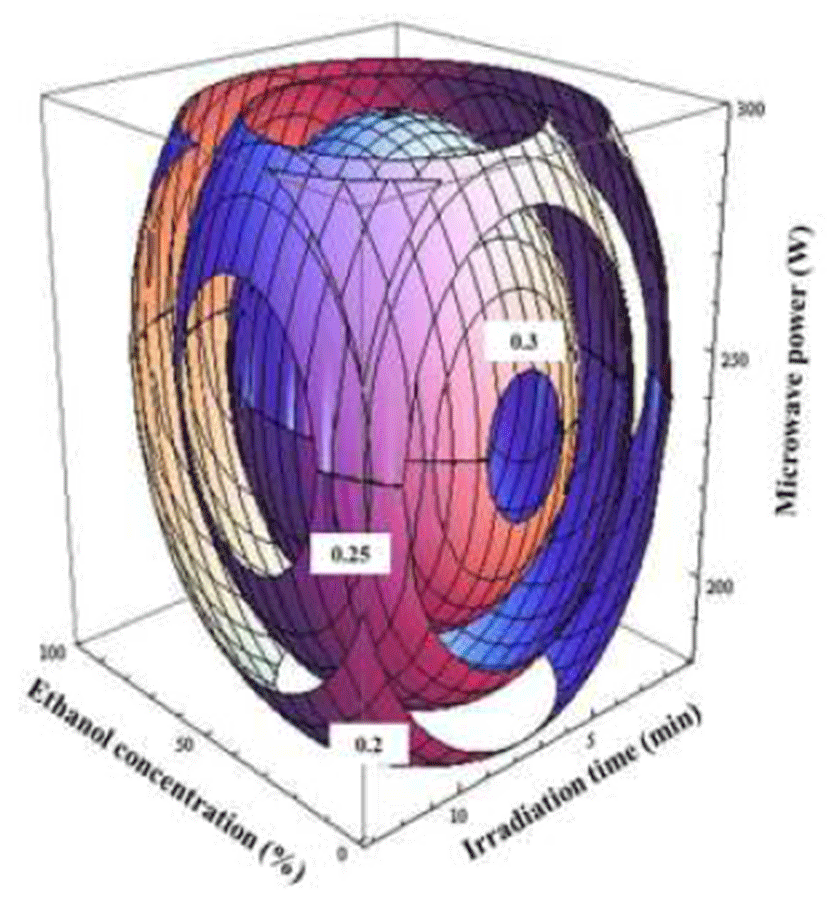
식품 유래 기능성물질의 대표적인 성분 중 하나로 플라 보노이드, 안토시아닌 등과 같은 페놀성분이 있다. 이들 폴리페놀은 한 분자 내에 2개 이상의 phenolic hydroxyl를 가진 방향족 화합물이며 항암, 항염증 등의 작용을 지니고 있는 항산화성 생리활성 물질이다(17,18). 중심합성계획법 에 의한 추출조건별 총 폴리페놀 함량은 Table 2에 나타내 었으며, 적합 모델식은 아래와 같다.
댕댕이 추출물의 총 폴리페놀 함량에 대한 회귀식의 R2 는 0.94이고 유의성은 0.1%이내의 수준에서 유의성을 나타 내었다. 추출물의 총 폴리페놀 함량에 대한 최대점은 에탄 올의 농도 56.9%, 추출시간 7.7분 및 microwave power 250 W 일 때 최대값은 14.71 mg GAE/g로 예측되었다(Table 5). Lee 등(19)의 참나무 겨우살이의 경우 물 추출물보다 에탄올 추출물의 총 폴리페놀 함량이 높게 나타나 본 실험 과 유사한 결과를 나타내었다. 총 폴리페놀 함량의 4차원 반응표면그래프(Fig. 4)는 ethanol농도가 57%, 추출시간이 7.7분, microwave power가 250 W에 가까울수록 함량이 증 가하는 것을 알 수 있었다. Pare 등(20)은 폴리페놀과 같은 목적성분을 추출하는 데 있어 마이크로웨이브 추출이 더 효과적이라고 하였으며, 이는 시료가 마이크로웨이브 에너 지에 노출됨으로써 시료 내부의 목적성분이 용매에 추출되 기 때문이라고 하였다.
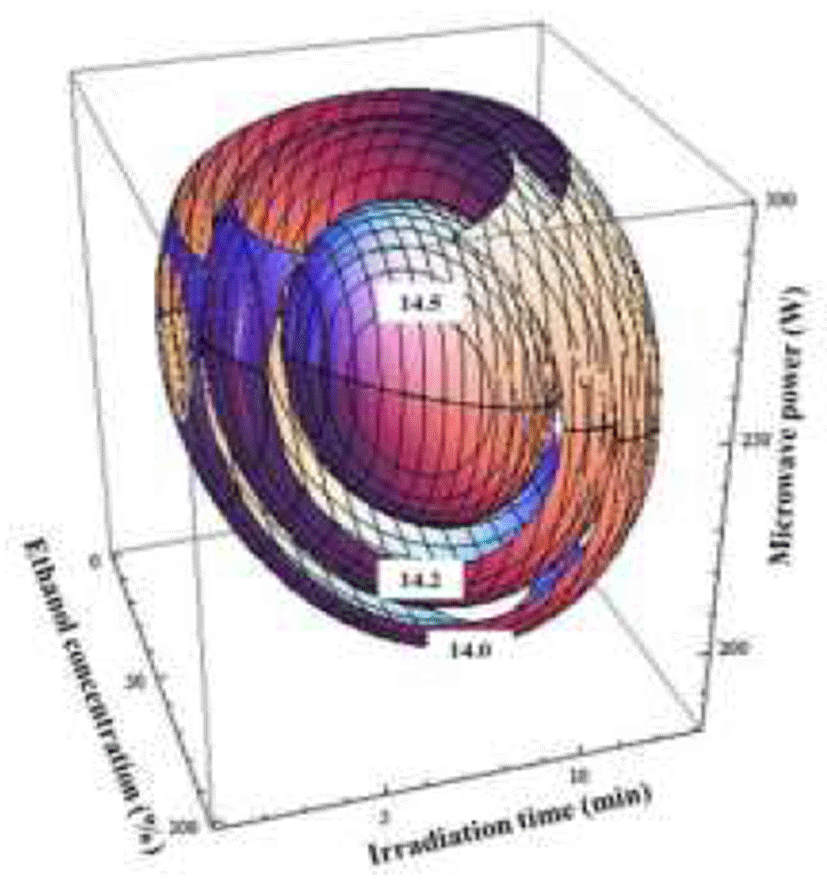
천연물의 DPPH 라디칼 소거능은 식품 중의 지방질 산화 를 억제하는 특성을 가지고 있으며, 인체 내에서는 활성 라디칼에 의한 노화를 억제시키는 역할을 하고 있다(21). 중심합성계획법에 의한 추출조건별 DPPH 라디칼 소거능 변화는 Table 2와 같으며 에탄올 농도, 추출 시간, 마이크로 웨이브 에너지에 따른 항산화능 변화의 적합 모델식은 아래 와 같다.
댕댕이 추출물의 항산화능에 대한 회귀식의 R2는 0.95이 고 유의성은 0.1%이내의 수준에서 유의성을 나타내었다. 추출물의 항산화능은 에탄올의 농도 64.10%, 추출시간 7.9 분 및 microwave power 242 W일 때 92.54%로 가장 높은 값을 나타내었으며(Table 5), 이러한 최대값을 나타내는 조 건을 벗어날수록 항산화능은 감소하는 경향을 나타내었다 (Fig. 5). 본 연구에서는 에탄올 농도가 30-60% 범위에서 가장 높은 항산화능을 나타냈는데(Fig. 5) Lee 등(22)의 포 도씨 추출물의 경우에도 본 연구와 유사하게 35-67% 에탄 올 농도 범위에서 가장 높은 항산화능을 보였다고 한다. 반면에 Joo 등(23)이 연구한 백지 추출물의 마이크로웨이브 추출조건에 따른 DPPH 라디칼 소거능의 변화에서는 물을 용매로 사용한 추출물의 항산화능이 더 높게 나타나 본 연구와 상이한 결과를 나타내었다.
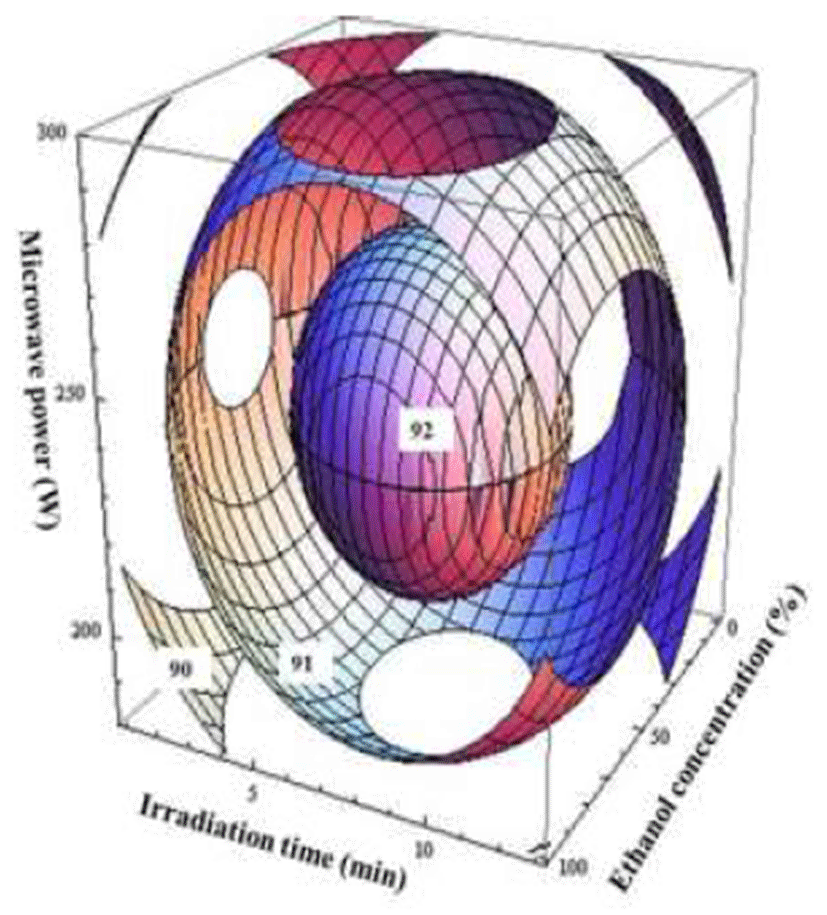
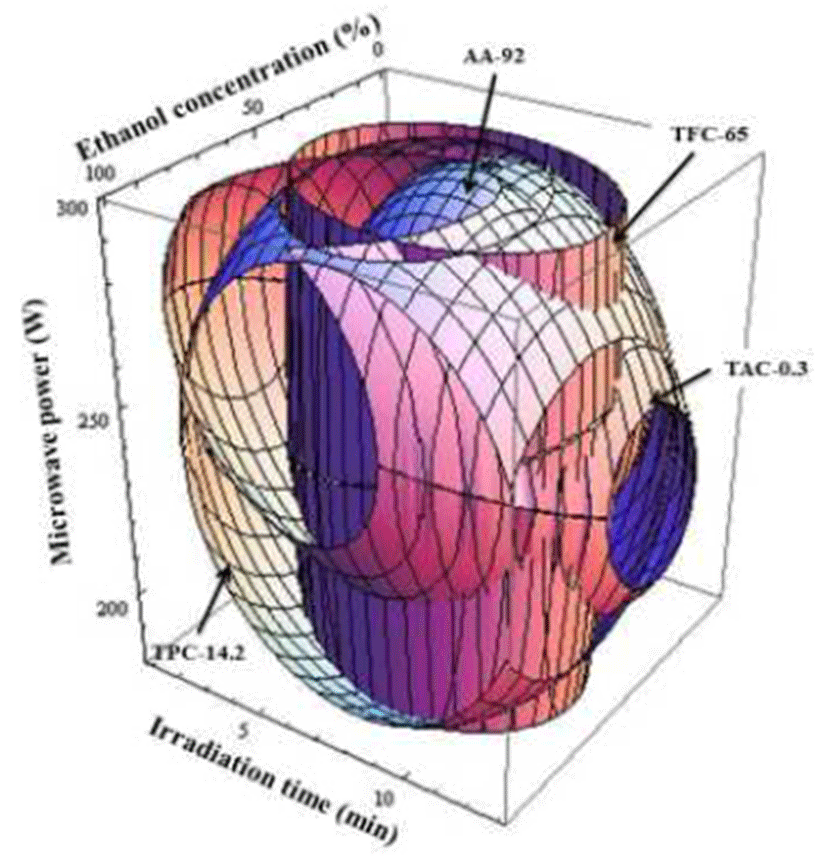
댕댕이의 기능성성분에 대한 최적 추출조건을 설정하기 위하여 각 조건별 추출물의 총 플라보노이드 함량, 총 안토 시아닌 함량, 총 폴리페놀 함량 그리고 항산화 활성의 contour maps를 superimposing하여 최적 범위를 예측하였다 (Fig. 6). 댕댕이 최적 추출조건 범위는 에탄올 농도53-64%, 추출시간 7.4-7.9 min, microwave power 242-250 W로 나타 났다(Table 5). 최적 조건 내에서 임의의 점 에탄올 농도 60%, 추출 시간 7.5 min, microwave power 245 W에 대입한 결과, TFC는 65.74 mg RE/g, TAC는 0.45 mg CGE/g, TPC는 14.71 mg GAE/g, DPPH는 92.54%의 수치로 나타냈다 (Table 6). 예측 결과에 대해 모델식을 검증하기 위해 주어진 임의의 조건에서 확인실험을 진행하였으며, 그 결과 TFC, TAC, TPC 그리고 DPPH는 각각 64.09 mg RE/g, 0.38 mg CGE/g, 14.29 mg GAE/g, 91.85%의 수치를 나타내었다 (Table 6).
| Response variables2) | Predicted value | Experimental value |
|---|---|---|
| TFC (mg RE/g) | 65.74 | 64.09 |
| TAC (mg CGE/g) | 0.45 | 0.38 |
| TPC (mg GAE/g) | 14.71 | 14.29 |
| DPPH (%) | 92.54 | 91.85 |
요 약
본 실험은 댕댕이의 마이크로웨이브 추출장치를 활용한 플라보노이드, 안토시아닌, 폴리페놀, 항산화능 등을 반응 표면분석법을 통하여 최적추출조건의 예측과 추출조건에 따른 추출물의 기능성 성분 함량을 모니터링 하였다. 중심 합성계획법을 통해 추출공정에 중요한 독립변수인 용액농 도(X1: 0, 25, 50, 75, 100%), 추출시간(X2: 1, 4, 7, 10, 13 min), microwave power(X3: 180, 210, 240, 270, 300 W)를 각각 독립변수로 설정하였고, 총 플라보노이드 함량(Y1), 총 안토시아닌 함량(Y2), 총 폴리페놀 함량(Y3) 그리고 DPPH 라디칼 소거능(Y4) 등을 종속변수로 하여 회귀분석 을 실시하였다. 예측된 최적조건 범위는 에탄올 농도 53-64%, 추출시간 7.4-7.9 min, microwave power 242-250 W로 나타났다. 플라보노이드 함량의 최대점은 에탄올의 농도 52.9%, 추출시간 7.5분, microwave power 244 W일 때 최대값은 65.74 mg RE/g으로 예측되었다. 안토시아닌 함량의 최대점은 에탄올의 농도 54.8%, 추출시간 7.4분, microwave power 248 W일 때 최대값은 0.45 mg CGE/g으로 예측되었다. 폴리페놀 함량의 최대점은 에탄올의 농도 56.9%, 추출시간 7.7분 및 microwave power 250 W 일 때 최대값은 14.71 mg GAE/g로 예측되었다. 항산화능의 최대 점은 에탄올의 농도 64.10%, 추출시간 7.9분 및 microwave power 242 W일 때 최대값은 92.54%로 예측되었다. 예측값 과 실험값의 차이가 거의 없는 것으로 보아 본 실험은 정확 도가 높고 신뢰성이 높음을 확인할 수 있었다. 이와 같은 결과는 댕댕이 마이크로웨이브 추출방법에 있어서 최적의 추출조건에 대한 정보를 주는 것이며, 더 나아가 고농도 댕댕이 기능성 성분이 함유된 제품 개발에 기초정보를 제공 하는 결과라 사료된다.










