ARTICLE
아선약 추출물의 matrix metalloproteinase-1(MMP-1) 억제 및 제1형 프로콜라겐 합성 촉진 활성
이재민1, 김동희2, 이은우3,4, 권현주3,4, 김병우3,4, 조재현5, 김현주6, 김태훈4,7,*
Matrix metalloproteinase-1 suppression and type-1 procollagen synthesis promoting effects of Uncaria gambir
Jaemin Lee1, Dong-Hee Kim2, Eun-Woo Kim3,4, Hyun Ju Kwon3,4, Byung Woo Kim3,4, Jae-Hyon Cho5, Hyun-Joo Kim6, Tae Hoon Kim4,7,*
4동의대학교 블루바이오 소재개발 및 실용화 지원센터
1Department of Oral Pathology, School of Dentistry, Kyungpook National University, Daegu 41940, Korea
2National Development Institute of Korean Medicine, Gyeongsan 38540, Korea
3Department of Life Science and Biotechnology, Dong-Eui University, Busan 47340, Korea
4Blue-Bio Industry Regional Innovation Center, Dong-Eui University, Busan 47340, Korea
5Institute of Animal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju 52828, Korea
6Crop Post-harvest Technology Division, National Institute of Crop Science, Rural Development Administration, Gyeonggi 16613, Korea
7Department of Food Science and Biotechnology, Daegu University, Gyeongsan 38453, Korea
© The Korean Society of Food Preservation. This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Received: Jul 27, 2016; Revised: Oct 24, 2016; Accepted: Oct 26, 2016
Abstract
Collagen synthesis is decreased and matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) levels are increased in naturally aged human skin, and these alterations cause changes such as skin wrinkling and decreased elasticity. As a part of our ongoing search for bioactive ingredients, MMP-1 inhibitory and type-1 procollagen synthesis inducing activities of aqueous methanolic extract of manufactured gambir product from Uncaria gambir were investigated in in vitro bioassay systems. In addition, total phenolic contents were quantified using a spectrophotometric method. Among tested samples, 40% MeOH eluate from 80% methanolic extract of manufactured U. gambir using open column chromatography packed with Diaion HP-20 resin showed significant MMP-1 inhibitory activities with an IC50 value of 15.6±1.3 μg/mL. Furthermore, type-1 procollagen synthesis promoting property of 40% MeOH eluate (IC50 value; 6.9±0.7 μg/mL) from 80% methanolic extract of manufactured gambir was higher than other eluates. Additionally, the present investigation revealed that 40% MeOH eluate of manufactured gambir product contained a high level of total phenolic compounds. The result suggests a distinct relationship between anti-wrinkle activity and total phenolic contents, and manufactured gambir product could be considered a new effective source of natural bioactive ingredients. Systematic investigation of manufactured gambir product will be performed for further development of its biological properties.
Keywords: Uncaria gambir; anti-wrinkle activity; matrix metalloproteinase-1; type-1 procollagen; phenolics
서 론
자외선(ultraviolet, UV)에 장기간 노출은 각종 피부 트러 블, 기미, 주근깨, 피부 색소 침착 등의 피부노화 현상 및 피부암 등의 피부 질환을 유발하며, 피부의 교원질 섬유인 collagen 및 elastin에 손상을 주어 태양에 노출된 피부의 주름 생성에 직접적으로 관여하는 것이 알려져 있다(1). 인체 피부의 기능적인 특성은 피부에서 가장 풍부하게 존재 하는 구조 단백질인 collagen의 상태와 관련이 깊으며, collagen은 피부에 강도와 장력을 부여하여 외부의 자극 등으로부터 피부를 보호하는 역할을 하고 collagen의 감소 는 피부의 노화 및 주름생성에 밀접하게 관여하는 성분으로 알려져 있다(2). 또한 인체 내의 collagen의 합성 및 분해 과정은 적절하게 조절되며, 노화가 진행되면서 collagen의 양이 감소하고 피부가 자외선에 노출되면 기질 단백질 분해 효소인 matrix metalloproteinases(MMPs)의 발현이 촉진된 다(3,4). MMP는 세포외 기질과 기저막의 분해에 관여하는 아연을 포함하는 단백질 분해 효소로서 구조 및 기능적 특성에 따라 collagenase, gelatinase, stromelysin, matrilysin 및 membrane type-MMP(MT-MMP) 등으로 구분된다(5). 또 한 MMP는 사이토카인, 자외선, 종양 유발 및 성장 인자들 을 포함하는 다양한 세포 외 자극에 의해 과발현 되는데, 이는 암 및 염증 등의 질병의 유발과정에도 영향을 주는 것이 보고된 바 있다(6). 피부에서의 콜라겐 함량은 가령화 에 따른 내인성 노화 및 자외선 노출에 의한 광노화에 의해 영향을 받으며, 피부의 노화가 진행됨에 따라 피부내의 MMP-1의 활성은 증가하는데, 이는 피부의 콜라겐 함량 감소를 통한 탄력 감소와 주름 생성을 유발한다(1,7). 따라 서 콜라겐 대사를 조절하는 소재의 탐색은 자외선으로부터 유도되는 피부 노화를 예방하고 치료하는데 효과적인 접근 방법으로 판단되고 있다.
아선약(Uncaria gambir )은 꼭두서니과(Rubiaceae)의 잎 및 어린 가지의 수제 추출액을 건조한 것으로 말레이군도 원산으로 Java, Sumatra, Borneo 지역에서 재배된다(8). 아 선약은 설사, 세균성 이질, 인후염 등의 치료를 위한 전통약 물로 동남아시아에서 오랫동안 사용되어져 왔다(9). 최근 의 연구 결과에 의하면 아선약의 주요 성분으로서 catechin 및 flavan dimer 관련물질을 포함하며, 미량 성분으로서는 indole alkaolid의 존재가 보고되어져 있다(10,11). 또한 아선 약은 catechin 및 catechin 유도체를 약 20-40% 전후로 함유 하고 있으며 최근 아선약의 품질 평가를 위한 아선약의 주요 catechin인 epicatechin, procyanidin B1, procyanidin B3, gambiriin A1에 대하여 HPLC를 활용한 정량 평가법이 보고 되어져 있다(12). 최근 아선약의 주요 성분인 catechin의 가열처리를 통하여 catechin 산화 축합반응에의한 catechin dimer 및 epicatechin의 생성과 이들 물질의 우수한 α -glucosidase 저해 활성을 나타냄이 보고되어져 있다(13). 아선약은 항산화, 항염증 등의 효능이 보고되어 있으나 본 천연소재의 생리활성과 관련된 보고는 극히 제한적이다 (14,15). 본 연구에서는 아선약의 메탄올 추출물 및 open column chromatography를 활용한 각 용리액에 대하여 주름 개선과 관련된 효소인 MMP-1 억제 및 type-1 procollagen 합성 촉진 활성을 평가하고 우수한 효능을 확인하였기에 그 결과를 보고하고자 한다.
재료 및 방법
재 료
본 실험에 시료로 사용한 아선약(Uncaria gambir)은 2011 년도 9월에 중국 후난성에서 채취 후 제조된 아선약을 사용 하였으며, 표본시료는 대구대학교의 식품공학과 천연물화 학실험실에 보관하고 있다. 본 실험에서 사용된 시약으로 procollagen typeⅠC-peptide EIA kit(Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan) 을 구입하여 사용하였고 MMP-1 활성을 측정하기 위하여 MMP-1 kit(Amersham Bioscience, Piseataway, USA), 구입하여 사용하였고, human fibroblast세포로 HS68 은 American Type Culture Collection(ATCC)에서 구입하여 사용하였다. 그 외에 사용된 용매 및 시약은 모두 일급 이상 의 등급을 사용하였다.
추출물의 제조 및 분획
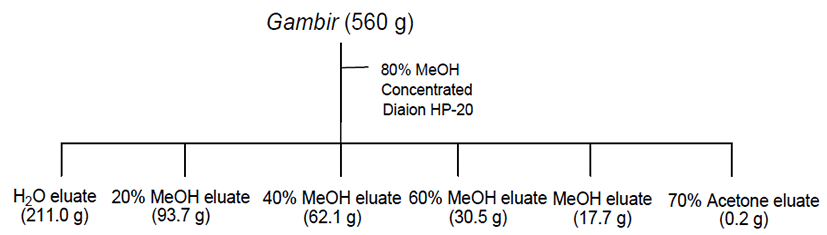
건조된 아선약 560 g을 잘게 마쇄하여 80% 메탄올(1L)로 실온에서 침지추출을 3회 반복하여 여과한 후 농축하였다. 얻어진 아선약 메탄올 추출물(430.5 g)에 대해 H2O 0.2L로 현탁하여 Diaion HP-20(2.8 cm i.d.×58 cm, Mitsubishi Chemical Co., Tokyo, Japan) 수지를 활용한 칼럼크로마토 그래피를 실시하여, H2O(211.0 g), 20% MeOH(93.7 g), 40% MeOH(62.1 g), 60% MeOH(30.5 g), MeOH(17.7 g) 및 70% acetone 용리액(0.2 g)을 얻었으며(Fig. 1), 각 분획물을 대상 으로 MMP-1 억제 및 type-1 procollagen 합성 촉진 활성 평가를 수행하였다.
세포독성 측정(MTT 실험)
세포 독성은 MMT(3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2yl)-2,5-diphenyl- 2H-tetrazolium bromide) 시약을 이용하여 세포 생존율을 측정하는 기존의 방법을 수정하여 사용하였다(16). 세포 배양은 10% fetal bovine serum(FBS)과 1% penicillin/ streptomycin(100 U/mL)을 첨가한 Dulbeccos's Modified Eagle's Medium(DMEM; Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) 배지를 사용하였으며 37℃, 5% CO2 incubator에 적응시켜 계대 배양하였다. MTT assay는 탈수소 효과작용에 의하여 노란색의 수용성 기질인 MMT tetrazolium을 청자색을 띄는 비수용성의 MMT formazan(3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)- 2,5-diphenyl- tetrazolium bromide)으로 환원시키는 미트콘 드리아의 능력을 이용한 검사법으로 MMT formazan의 농 도를 540 nm에서 ELISA plate reader(Tecan Austria GmBH, Grödig, Austria)를 이용하여 측정하였다.
MMP-1 저해 활성 측정
배양액 안의 MMP-1 단백질의 함량은 시판 ELISA kit(R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA)를 사용하여 측정 하였다. 먼저 MMP-1 kit의 표준 용액은 1/2 희석하였고, 표준 용액 100 μL와 시료 100 μL를 MMP-1 ELISA kit의 micro plate 분주하고 100 μL horseradish peroxidase conjugate 를 첨가한 후 2시간 동안 37℃에서 배양하였다. 완충 용액으 로 각 well을 5회 반복 세척하여 비결합 항원을 제거한 후 100 μL 의 chromogenic tetramethyl benzidine을 넣어 30분간 반응시켰다. 그 후 100 μL의 정지 시약을 넣고 15분 후에 450 nm에서 ELISA plate reader(Tecan Austria GmBH)를 이용하여 흡광도를 측정하였다(17).
Type-1 procollagen 합성 촉진 활성 측정
CCD-986sk 세포를 24-well plate에 5×104 cell/well의 농도 로 접종한 후 24시간 배양하였다. 세포를 phosphate buffered saline(PBS)로 2회 세척한 후 무혈청 배양액을 첨가한다. 24시간 후 시료를 처리하고 48시간 동안 배양한다. 배양액 을 수집하여 측정에 사용하였다. 세포배양액 내의 콜라겐 합성 정도는 procollagen type I C-peptide assay kit(Takara Bio Inc.)를 사용하여 콜라겐의 함량을 측정하였다(18).
총페놀성 화합물 함량 평가
총 페놀성 화합물의 함량은 Folin-Denis 방법(19)에 따라 측정하였으며, 추출물 혹은 분획물을 1.0 mg/mL 농도로 조제한 후, 시료 50 μL와 Folin-Denis 시액 50 μL, 0.7 M 탄산나트륨 포화용액 50 μL를 차례로 넣은 다음 이것을 잘 혼합하여 실온에서 60분 방치한 후 UV/VIS 분광광도계 (Jasco V-710, Tokyo, Japan)로 750 nm에서 흡광도를 측정하 였으며, 표준물질은 gallic acid를 이용하여 표준곡선을 작 성하여 양을 환산하였다.
통계처리
결과 통계처리는 SPSS 12.0(Version 12, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA)을 사용하였으며, 유의차 검증은 분산분 석(ANOVA, analysis of variance) 프로그램을 이용하여 Duncan’s multiple range test를 이용하여 통계적 유의수준 p<0.05에서 검증하였다.
결과 및 고찰
MTT assay에 의한 세포 생존율 측정
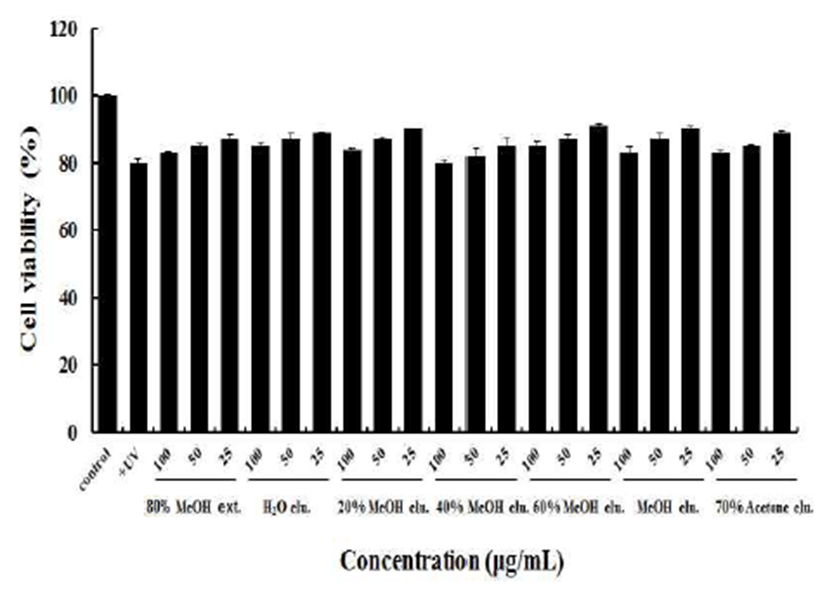
건조된 아선약의 80% 메탄올 추출물에 대해 Diaion HP-20 수지를 충진한 칼럼크로마토그래피를 실시하여 얻 어진 H2O, 20% MeOH, 40% MeOH, 60% MeOH, MeOH 및 70% acetone 용리액에 대하여 human dermal fibroblast HS68 세포의 증식에 미치는 영향을 평가한 결과는 Fig. 2와 같다. 아선약의 80% 메탄올 추출물과 각 용매별 용리액 을 농도별로 처리한 후 HS68 세포를 48시간동안 배양하여 세포생존율을 측정한 결과, 아선약 80% 메탄올 추출물 및 각 용리액에서 25, 50, 100 μg/mL의 농도에서 세포생존율이 80% 이상으로 세포독성이 없는 것으로 나타났으므로 이들 농도에서 활성 평가를 수행하였다.
Fig. 2.
Cell viability of HS68 fibroblast cells of gambir extract and eluates.
Data are expressed as the mean value±SD (n=3) of triplicate experiments.
Download Original Figure
MMP-1 저해 활성 측정
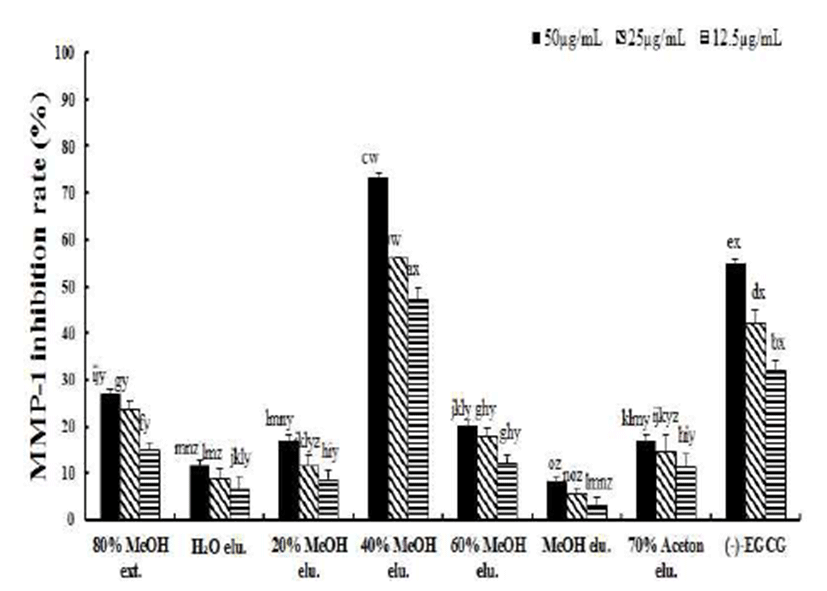
Collagen은 피부세포의 결합 조직을 구성하는 주요 성분 중 피부 건조 중량의 약 70-80% 정도를 차지하는 주요 구성 단백질이다. 그러므로 인체 결합조직에서 collagen의 분해 는 피부의 탄력저하와 주름생성 등에 직접적인 영향을 미친 다. 인체에서 생성되는 여러 종류의 MMP들 중에 MMP-1은 collagen에 특이하게 작용하는 단백질 분해효소로서 MMP-1을 저해 하는 것으로, 이는 생체의 collagen의 분해를 감소시키며 피부조직의 탄력을 강화하고 주름생성을 방지 할 수 있는 좋은 전략으로 알려져 있다(20). 본 연구에서 아선약 및 각 용리액에 대한 MMP-1 저해활성을 평가한 결과(Fig. 3), 아선약 80% 메탄올 추출물은 50 μg/mL의 농도 에서 27.1±1.2%의 저해활성을 나타내었으며, Diaion HP-20 수지를 활용한 칼럼크로마토그래피 용리액 중 40% MeOH 용리액에서 IC50값은 15.6±1.3 μg/mL의 우수한 활성을 나타 내었으며, 이 활성은 positive control로 사용된 녹차의 주름 개선 성분인 (-)-epigallocatechin gallate(EGCG)의 IC50값은 38.4±2.3 μg/mL 보다 우수한 활성이었다. 한편, 20% MeOH, 60% MeOH 및 70% acetone 용리액은 50 μg/mL의 농도에서 각각 16.7±1.3%, 20.3±1.5% 및 17.2± 1.1%의 상대적으로 약한 저해활성을 나타내었다. 최근 flavonoid, stilbenoid, lignan 등의 페놀성 화합물은 MMP-1 저해 활성을 나타내는 주요성분(18,21,22)으로 보고 되어져 있으며, 이들 보고를 근거로 하여 페놀성 화합물의 함량과 MMP-1 저해활성과 의 연관성을 평가한 결과, Table 1에서 나타낸 것처럼, MMP-1 저해활성이 우수한 40% MeOH 용리액에 총페놀성 화합물의 함량이 99.4±5.7 mg/g으로 가장 높게 나타났으며, 40% MeOH 용리액에 MMP-1 저해활성이 positive control보 다 강한 우수한 페놀성 화합물의 존재를 시사하였다. 현재 까지의 연구결과에 의하면 천연에 광범위하게 존재하는 페놀성 화합물의 일종인 플라보노이드계 화합물 중 MMP-1에 효과적인 물질로, 황금(Scutellaria baicalensis)의 flavone glycoside인 baicalin(23), 녹차(Camellia sinensis)의 주요flavan-3-ol 화합물인(-)-EGCG(24), 과일 및 채소에 함유 되어 있는 anthocyanin 화합물(25) 등이 알려져 있다. 이들 보고된 화합물 이외의 아선약에 존재하는 페놀성 화합물의 주름개선 효능과 관련된 MMP-1의 저해활성성분의 분리 및 동정을 통한 추가적 연구가 필요하다고 사료된다.
Fig. 3.
Inhibitory effects of the tested sample of gambir on MMP-1.
EGCG was used as a positive control. Data are expressed as the mean value±SD (n=3) of triplicate experiments. The different letters indicate significant differences determined by Duncan’s multiple range test (p<0.05).
Download Original Figure
Table 1.
Total phenolic contents of the methanolic extract and organic solvent eluates of gambir
|
Samples |
Phenolic contents (mg/g) |
|
MeOH ext. |
68.7±3.11)c2) |
|
H2O eluate |
53.3±2.7d
|
|
20% MeOH eluate |
63.7±2.7c
|
|
40% MeOH eluate |
99.4±5.7a
|
|
60% MeOH eluate |
78.2±4.2b
|
|
MeOH eluate |
62.1±3.0c
|
|
70% Acetone eluate |
45.7±2.8e
|
Download Excel Table
Type-1 procollagen 합성 촉진 활성 측정
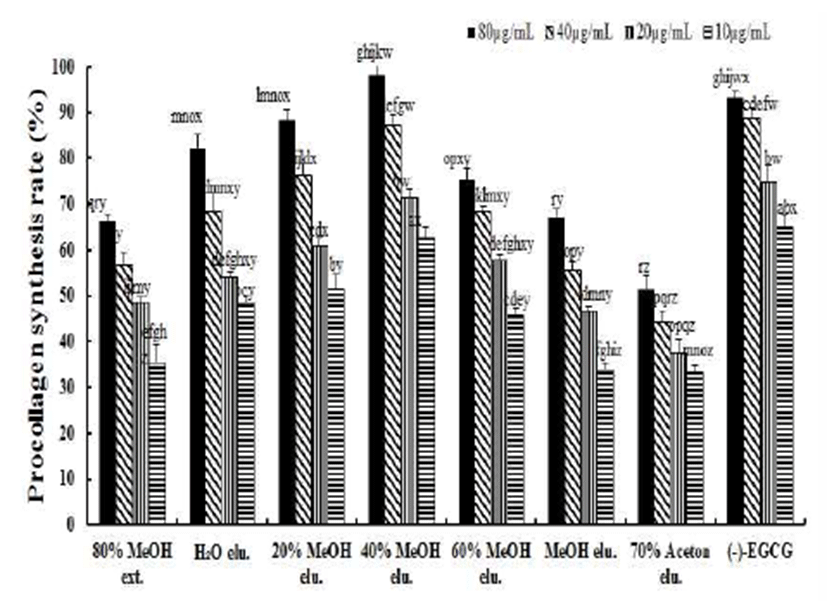
피부상피세포 건조중량의 약 70-80%를 차지하는 주요구 성 성분인 collagen은 elastin 및 hyaluronic acid와 함께 피부 의 탄력 및 주름관련 주요 성분으로 알려져 있다. 일반적으 로 피부에서 type 1 collagen의 합성과 분해 효소의 하나인 MMP-1의 활성이 균형을 이루고 있지만, 내외부적인 요인 에 의하여 피부 노화가 진행되는 피부조직에서는 type 1 collagen의 합성이 저하되고 MMP-1의 효소 활성이 증가되 는 것이 알려져 있다(26). 그러므로 collagen 합성 촉진 효능 은 주름 방지를 위한 효과적인 방법이라 판단된다. 본 연구 에서 아선약의 type 1 collagen의 합성 촉진 효능평가를 수행 한 결과(Fig. 4), 아선약의 80% 메탄올 추출물의 EC50값은 25.8±1.4 μg/mL의 효능을 나타내었고, Diaion HP-20 수지 를 활용한 칼럼크로마토그래피 용리액 중 40% MeOH 용리 액 경우 EC50값이 6.9±0.7 μg/mL의 상대적으로 강한 활성을 나타났다. 양성대조구인 (-)-EGCG의 EC50값이 5.5±0.9 μ g/mL과 비교해볼 때 40% MeOH 용리액 경우는 우수한 효능을 나타냄을 확인하였다. 한편, 20% MeOH, 60% MeOH 및 H2O 용리액의 EC50값은 각각 10.2±1.4 μg/mL, 12.7±0.6 μg/mL 및 12.8±1.2 μg/mL의 상대적으로 약한 type 1 collagen 합성 촉진 활성을 나타내었다. 최근 천연소재로 부터 type 1 procollagen 생합성능이 우수한 주름개선 소재 발굴을 위하여 진행된 연구에 의하면 때죽나무(Styrax japonica)의 triterpenoid인 erythrodiol-3-acetate은 1 μM에서 223.7±11%의 type 1 procollagen 증가를 유도하였으며(27), 강황 추출물의 경우 0.5 μM에서 196%의 type 1 procollagen 증가를 유도하였으며, 활성성분은 sesquiterpenoid인 xanthorrhizol로 동정하였다(28). 이상의 결과 및 최근의 type 1 procollagen 생합성 촉진 활성과 관련된 화합물의 aglycone은 대부분이 terpenoid 유도체가 주로 보고(29,30) 되어져 있으나 아선약의 활성성분으로 추정되는 페놀성 화합물(10,12)의 분리, 동정 및 활성기작 평가를 통하여 아 선약 추출물의 우수한 주름개선 소재로서의 추가적인 연구 가 필요하다고 사료된다.
Fig. 4.
Effects of the isolated constituents on Type I collagen synthesis in UVB-ir radiated human fibroblast cells.
UV (20 mJ/cm2)-exposed cells were cultured for 48 h in the presence of tested samples. EGCG was used as a positive control. Data are expressed as the mean value±SD (n=3) of triplicate experiments. The different letters indicate significant differences determined by Duncan’s multiple range test (p<0.05).
Download Original Figure
총페놀성 화합물 함량
아선약의 함수 메탄올 추출물 및 각 용리액이 함유하고 있는 총페놀성 화합물의 함량을 Table 1에서 나타내었으며, 아선약 80% 메탄올 추출물은 1 g당 68.7±3.1 mg의 총페놀 성 화합물의 함유량을 확인하였다. Diaion HP-20 수지를 활용한 용리액의 경우 40% 메탄올 용리액이 68.7±5.7 mg/g 의 가장 높은 함량을 나타내었으며, 60% 메탄올 용리액 > 20% 메탄올 용리액 > 메탄올 용리액 > H2O 용리액 > 70% acetone 용리액의 순으로 총페놀성 화합물 함유량이 감소함을 확인하였다. 이상의 결과로부터 아선약 함수 메 탄올 추출물의 MMP-1 저해 및 type-1 procollagen 합성 촉진 활성은 Fig. 3, 4 및 Table 1에서 나타낸 것처럼 총페놀성 화합물 함유량이 상대적으로 높은 40% 메탄올 용리액 상태 에서 positive control인 (-)-EGCG 보다 우수하거나 동일한 수준의 상대적으로 높은 것을 확인할 수 있었으며, 아선약 의 80% 메탄올 추출물의 MMP-1 저해 및 type-1 procollagen 합성 촉진 활성과 페놀성 화합물 함량 사이에는 밀접한 상관관계가 있음을 시사하였다.
요 약
건조한 아선약을 80% 메탄올로 침지 추출하여 얻어진 추출물에 대해 Diaion HP-20 수지를 충진제로 사용한 칼럼 크로마토그래피를 수해하여 6종의 용리액을 얻었으며, 얻 어진 추출물에 대하여 MMP-1 저해 및 type-1 procollagen 합성 촉진 활성을 평가하였다. 먼저 MMP-1 저해활성은 총페놀성 화합물의 함량이 상대적으로 높은 40% 메탄올 용리액에서 IC50값이 15.6±1.3 μg/mL으로 positive control로 녹차의 주름개선 성분인 (-)-EGCG의 IC50값인 38.4±2.3 μ g/mL 보다 우수한 활성이었다. 또한 type-1 procollagen 합성 촉진 활성은 총페놀성 화합물 함량이 가장 높은 40% 메탄 올 용리액에서 우수한 EC50값이 6.9±0.7 μg/mL을 나타내었 으며, 양성대조구인 (-)-EGCG의 효능과 동등한 활성이었 다. 본 실험에 사용된 아선약 시료의 경우 다양한 화합물이 공존하는 추출물 및 용리액 상태이며 이들 시료에 우수한 효능의 성분의 존재 및 추출물에 존재하는 화합물의 우수한 상승효과의 가능성을 시사하였다. 향후 각종 칼럼크로마토 그래피를 활용한 이들 주름개선 효능 관련 물질의 분리를 통한 활성물질의 구조 결정 및 활성 기작에 대한 연구를 수행할 예정이며, 본 연구결과는 천연물 유래의 우수한 MMP-1 저해 및 type-1 procollagen 합성 촉진 활성을 가지는 새로운 천연 소재 발굴을 위한 기초자료로 활용 가능할 것으로 사료된다.
감사의 글
이 연구는 산업통상자원부ㆍ부산광역시 지원 지역혁신 센터사업(RIC08-06-07) 동의대학교 블루바이오 소재개발 및 실용화지원센터의 지원으로 이루어졌습니다.
References
Fisher GJ, Datta SC, Talwar HS, Wang ZQ, Varani J, Kang S, Voorhees JJ. Molecular basis of sun-induced premature skin ageing and retinoid antagonism. Nature. 1996; 379:335-339


Kavitha O, Thampan RV. Factors influencing collagen biosynthesis. J Cell Biochem. 2008; 104:1150-1160


Scharffetter K, Wlaschek M, Hogg A, Bolsen K, Schothorst A, Goerz G, Krieg T, Plewig G. UVA irradiation induces collagenase in human dermal fibroblasts in vitro and in vivo. Arch Dermatol Res. 1991; 283:506-511


Chung JH, Seo JY, Choi HR, Lee MK, Youn CS, Rhie GE, Cho KH, Kim KH, Park KC, Eun HC. Modulation of skin collagen metabolism in aged and photoaged human skin in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 2001; 117:1218-1224


Visse R, Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res. 2003; 92:827-839


Sternlicht MD, Werb Z. How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2001; 17:463-516


Varani J, Warner RL, Gharaee-Kermani M, Phan SH, Kang S, Chung JH, Wang ZQ, Datta SC, Fisher GJ, Voorhees JJ. Vitamin A antagonizes decreased cell growth and elevated collagen-degrading matrix metalloproteinases and stimulates collagen accumulation in naturally aged human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2000; 114:480-486


Risdale CE. A revision of Mitragyna and Uncaria (Rubiaceae). Blumea. 1978; 24:43-100.

Perry LM, Metzger J. Medicinal Plants of East and Southeast Asia arributed properties and uses. 1980; MIT press. Cambridge, MA, USA: p. 395.

Taniguchi S, Kuroda K, Doi K, Tanabe M, Shibata T, Yoshida T, Hatano T. Revised structures of gambiriins A1, A2, B1, and B2, chalcane-flavan dimers from gambir (Uncaria gambir extract). Chem Pharm Bull. 2007; 55:268-272


Chen KC. Gambirdine and isogambirdine, the alkaloids from Uncaria gambir (Hunt) Roxb. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968; 30:3403-3406.

Taniguchi S, Kuroda K, Doi K, Inada K, Yoshikado N, Yoneda Y, Tanabe M, Shibata T, Yoshida T, Hatano T. Evaluation of gambir quality based on quantitative analysis of polyphenolic constituents. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007; 127:1291-1300


Kim TW, Choi HJ, Eom SH, Lee JM, Kim TH. Potential ?-glucosidase inhibitors from thermal transformation of (+)-catechin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014; 24:1621-1624


Yimam M, Lee YC, Kim TW, Moore B, Jiao P, Hong M, Kim HJ, Nam JB, Kim MR, Oh JS, Cleveland S, Hyun EJ, Chu M, Jia Q. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect of UP3005, a botanical composition containing two standardized extracts of Uncaria gambir and Morus alba. Pharmacognosy Res. 2015; 7:S39-46


Sazwi NN, Nalina T, Abdul Rahim ZH. Antioxidant and cytoprotective activities of Piper betle, Areca catechu, Uncaria gambir and betel quid with and without calcium hydroxide. BMC complementary Altern Med. 2013; 13:351-362.

Carmichael J, DeGraff WG, Gazdar AF, Minna JD Mitchell JB. Evaluation of a tetrazolium based semiautomated colorimetric assay assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer Res. 1987; 47:936-942.

Gross J, Lapiere CM. Collagenolytic activity in amphibian tissues a tissue culture assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1962; 48:1014-1022


Park EK, Ahn SR, Kim DH, Lee EW, Kwon HJ, Kim BW, Kim TH. Effects of unripe apple polyphenols on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and type-1 procollagen in ultraviolet irradiated human skin fibroblasts. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem. 2014; 57:449-455


Singleton VL, Orthofer R, Lamuela-Raventos RM. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substratesand antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999; 299:152-178.

Nagase H, Woessner JF. Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:21491-21494.

Abe N, Ito T, Ohguchi K, Nasu M, Mastuda Y, Oyama M, Nozawa Y, Ito M, Iinuma M. Resveratrol oligomers from Vatica albiramis. J Nat Prod. 2010; 73:1499-1506


Kim MR, Moon HI, Chung JH, Moon YH, Hahm KS, Woo ER. Matrix metalloproteinase-1 inhibitor from the stem bark of Styrax japonica S et Z. Chem Pharm Bull. 2004; 52:1466-1469


Min W, Liu X, Quin Q, Lin B, Wu D, Wang M, Ahmad I, Yusuf N, Luo D. The effects of baicalin against UVA-induced photoaging in skin fibroblasts. Am J Chin Med. 2014; 42:709-727


Kim JE, Shin MH, Chung JH. Epigallocatechin- 3-gallate prevents heat shock-induced MMP-1 expression by inhibiting AP-1 activity in human dermal fibroblasts. Arch Dermatol Res. 2013; 305:595-602


Lim TG, Jung SK, Kim JE, Kim Y, Lee HJ, Jang TS, Lee KW. NADPH oxidase is a novel target ofdelphinidin for the inhibition of UVB-induced MMP-1 expression in human dermal fibroblasts. Exp Dermatol. 2013; 22:428-430


Talwar HS, Griffiths CEM, Fisher GJ, Hamilton TA, Voorhees JJ. Reduced type I and type III procollagens in photodamaged adult human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1995; 105:285-290


Moon HI, Lee J, Chung JH. The effect of erythrodiol-3-acetate on the expressions of matrixmetalloproteinase-1 and type-1 procollagen caused by ultraviolet irradiated cultured primary old aged human skin fibroblasts. Phytomedicine. 2006; 13:707-711


Oh HI, Shim JS, Gwon SH, Kwon HJ, Hwang JK. The effect of xanthorrhizol on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1 and type-I procollagen in ultravioletirradiated human skin fibrobalsts. Phytother Res. 2009; 23:1299-1302.

Hong YF, Lee HY, Jung BJ, Jang S, Chung DK, Kim H. Lipoteichoic acid isolated from Lactobacillus plantarum down-regulates UV-induced MMP-1 expression and up-regulates type I procollagen through the inhibition of reactive oxygen species generation. Mol Immunol. 2015; 67:248-255


Kim YH, Chung CB, Kim JG, Ko KI, Park SH, Kim JH, Eom SY, Kim YS, Hwang YI, Kim KH. Anti-wrinkle activity of ziyuglycoside I isolated from a Sanguisorba officinalis root extract and its application as a cosmeceutical ingredient. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2008; 72:303-311